Sorting out functions of sirtuins in cancer
- PMID: 23604120
- PMCID: PMC4295628
- DOI: 10.1038/onc.2013.120
Sorting out functions of sirtuins in cancer
Abstract
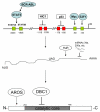
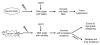
The sirtuins (SIRT 1-7) comprise a family of NAD⁺-dependent protein-modifying enzymes with activities in lysine deacetylation, adenosinediphospho(ADP)-ribosylation, and/or deacylation. These enzymes are involved in the cell's stress response systems and in regulating gene expression, DNA damage repair, metabolism and survival. Sirtuins have complex roles in both promoting and/or suppressing tumorigenesis. This review presents recent research progress concerning sirtuins and cancer. On one hand, functional loss of sirtuin genes, particularly SIRT1, involved in maintaining genome integrity and DNA repair will promote tumorigenesis because of genomic instability upon their loss. On the other hand, cancer cells tend to require sirtuins for these same processes to allow them to survive, proliferate, repair the otherwise catastrophic genomic events and evolve. The bifurcated roles of SIRT1, and perhaps several other sirtuins, in cancer may be in part a result of the nature of the genes that are involved in the cell's genome maintenance systems. The in-depth understanding of sirtuin functions may have significant implication in designing precise modulation of selective sirtuin members to aid cancer prevention or treatment under defined conditions.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sirtuins in metabolism, DNA repair and cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Dec 5;35(1):182. doi: 10.1186/s13046-016-0461-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27916001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sirtuins in Cancer: a Balancing Act between Genome Stability and Metabolism.Mol Cells. 2015 Sep;38(9):750-8. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2015.0167. Epub 2015 Sep 18. Mol Cells. 2015. PMID: 26420294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repairing split ends: SIRT6, mono-ADP ribosylation and DNA repair.Aging (Albany NY). 2011 Sep;3(9):829-35. doi: 10.18632/aging.100389. Aging (Albany NY). 2011. PMID: 21946623 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation and inhibition of sirtuins: From bench to bedside.Med Res Rev. 2025 Mar;45(2):484-560. doi: 10.1002/med.22076. Epub 2024 Aug 31. Med Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 39215785 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mammalian Sirtuins SIRT4 and SIRT7.Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018;154:147-168. doi: 10.1016/bs.pmbts.2017.11.001. Epub 2018 Jan 19. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci. 2018. PMID: 29413176 Review.
Cited by
-
Different Toxicity Mechanisms for Citrinin and Ochratoxin A Revealed by Transcriptomic Analysis in Yeast.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Sep 22;8(10):273. doi: 10.3390/toxins8100273. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27669300 Free PMC article.
-
In silico drug discovery of SIRT2 inhibitors from natural source as anticancer agents.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 7;13(1):2146. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-28226-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36750593 Free PMC article.
-
AG1031 induces apoptosis through suppressing SIRT1/p53 pathway in human neuroblastoma cells.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;454(1-2):165-175. doi: 10.1007/s11010-018-3461-2. Epub 2018 Oct 22. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30350304
-
Exploration of the Fluorescent Properties and the Modulated Activities against Sirtuin Fluorogenic Assays of Chromenone-Derived Natural Products.Molecules. 2018 May 2;23(5):1063. doi: 10.3390/molecules23051063. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 29724067 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of sirtuins on tumorigenesis: possible link between aging and cancer.BMB Rep. 2013 Sep;46(9):429-38. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.9.180. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 24064057 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M, Guarente L. Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 2000;403(6771):795–800. - PubMed
-
- Frye RA. Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2000;273(2):793–8. - PubMed
-
- Morris BJ. Seven sirtuins for seven deadly diseases of aging. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

