Antifungal Azoles: Structural Insights into Undesired Tight Binding to Cholesterol-Metabolizing CYP46A1
- PMID: 23604141
- PMCID: PMC3684827
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.113.085902
Antifungal Azoles: Structural Insights into Undesired Tight Binding to Cholesterol-Metabolizing CYP46A1
Abstract
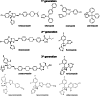
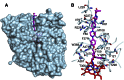
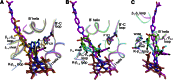
Although there are currently three generations of antifungal azoles on the market, even the third-generation agents show undesirable interactions with human cytochrome P450 (P450) enzymes. CYP46A1 is a cholesterol-metabolizing P450 in the brain that tightly binds a number of structurally distinct azoles. Previously, we determined the crystal structures of CYP46A1 in complex with voriconazole and clotrimazole, and in the present work we cocrystallized the P450 with posaconazole at 2.5 Å resolution. This long antifungal drug coordinates the P450 heme iron with the nitrogen atom of its terminal azole ring and adopts a linear configuration occupying the whole length of the substrate access channel and extending beyond the protein surface. Numerous drug-protein interactions determine the submicromolar Kd of posaconazole for CYP46A1. We compared the crystal structure of posaconazole-bound CYP46A1 with those of the P450 in complex with other drugs, including the antifungal voriconazole and clotrimazole. We also analyzed the accommodation of posaconazole in the active site of the target enzymes, CYPs 51, from several pathogenic species. These and the solution studies with different marketed azoles, collectively, allowed us to identify the determinants of tight azole binding to CYP46A1 and generate an overall picture of azole binding to this important P450. The data obtained suggest that development of CYP51-specific antifungal agents will continue to be a challenge. Therefore, structural understanding of the azole binding not only to CYPs 51 from the pathogenic species but also to different human P450s is required to deal efficiently with this challenge.
Figures


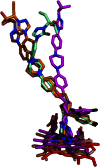
Similar articles
-
Structural basis of drug binding to CYP46A1, an enzyme that controls cholesterol turnover in the brain.J Biol Chem. 2010 Oct 8;285(41):31783-95. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.143313. Epub 2010 Jul 28. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20667828 Free PMC article.
-
The antifungal drug voriconazole is an efficient inhibitor of brain cholesterol 24S-hydroxylase in vitro and in vivo.J Lipid Res. 2010 Feb;51(2):318-23. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M900174-JLR200. Epub 2009 May 27. J Lipid Res. 2010. PMID: 19474457 Free PMC article.
-
Clotrimazole as a potent agent for treating the oomycete fish pathogen Saprolegnia parasitica through inhibition of sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51).Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014 Oct;80(19):6154-66. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01195-14. Epub 2014 Aug 1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 25085484 Free PMC article.
-
A new, broad-spectrum azole antifungal: posaconazole--mechanisms of action and resistance, spectrum of activity.Mycoses. 2006;49 Suppl 1:2-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1439-0507.2006.01295.x. Mycoses. 2006. PMID: 16961575 Review.
-
Fungal Lanosterol 14α-demethylase: A target for next-generation antifungal design.Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020 Mar;1868(3):140206. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2019.02.008. Epub 2019 Mar 6. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom. 2020. PMID: 30851431 Review.
Cited by
-
Complexes of Trypanosoma cruzi sterol 14α-demethylase (CYP51) with two pyridine-based drug candidates for Chagas disease: structural basis for pathogen selectivity.J Biol Chem. 2013 Nov 1;288(44):31602-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.497990. Epub 2013 Sep 18. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24047900 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping of the Allosteric Site in Cholesterol Hydroxylase CYP46A1 for Efavirenz, a Drug That Stimulates Enzyme Activity.J Biol Chem. 2016 May 27;291(22):11876-86. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.723577. Epub 2016 Apr 7. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27056331 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacologic stimulation of cytochrome P450 46A1 and cerebral cholesterol turnover in mice.J Biol Chem. 2014 Feb 7;289(6):3529-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.532846. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24352658 Free PMC article.
-
Identification, modeling and ligand affinity of early deuterostome CYP51s, and functional characterization of recombinant zebrafish sterol 14α-demethylase.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Jun;1840(6):1825-36. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.12.009. Epub 2013 Dec 19. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 24361620 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 requires cholesterol for viral entry and pathological syncytia formation.Elife. 2021 Apr 23;10:e65962. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65962. Elife. 2021. PMID: 33890572 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arnold TM, Dotson E, Sarosi GA, Hage CA. (2010) Traditional and emerging antifungal therapies. Proc Am Thorac Soc 7:222–228 - PubMed
-
- Björkhem I, Lütjohann D, Breuer O, Sakinis A, Wennmalm A. (1997) Importance of a novel oxidative mechanism for elimination of brain cholesterol. Turnover of cholesterol and 24(S)-hydroxycholesterol in rat brain as measured with 18O2 techniques in vivo and in vitro. J Biol Chem 272:30178–30184 - PubMed
-
- Collaborative Computational Project, Number 4 (1994) The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallography. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 50:760–763 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

