Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails
- PMID: 23604648
- PMCID: PMC4117878
- DOI: 10.1007/s11999-013-2963-1
Healing delayed but generally reliable after bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures treated with IM nails
Abstract
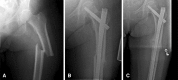
Background: Bisphosphonate therapy for osteoporosis has been associated with atypical femoral fractures. To date, there have been few reports in the literature regarding the preoperative and postoperative courses of patients who have sustained bisphosphonate-associated complete atypical femur fractures.
Objectives/purposes: The purposes of this study were to (1) characterize the preoperative course of patients who eventually presented with bisphosphonate-associated complete atypical femur fractures (duration of bisphosphonate treatment, pain history, risk of converting a nondisplaced fracture to a complete fracture); (2) evaluate the percentage of patients who achieved radiographic union of those fractures after treatment; and (3) determine the patients' recovery of function using the Short Musculoskeletal Functional Assessment.
Methods: Thirty-three patients with 41 atypical, low-energy femur fractures associated with ≥ 5 years of bisphosphonate use were treated with intramedullary nailing between 2004 and 2011 at one center. The main outcome measurements were Short Musculoskeletal Functional Assessment for function and radiographic evaluation for fracture healing. Patients had been treated with bisphosphonates for an average of 8.8 years (range, 5-20 years) before presentation.
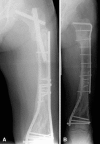
Results: Patients reported a mean of 6 months of pain before presentation (range, 1-8 months). Sixty-six percent of patients with surgically treated complete fractures became pain-free and 98% were radiographically healed by 12 months. Sixty-four percent of patients who underwent intramedullary nailing reported a functional return to baseline within 1 year. Patients who reported major functional limitations at latest followup listed pain and apprehension as the major causes of their limitation.
Conclusions: Patients with surgically treated bisphosphonate-associated complete femur fractures achieved generally reliable although delayed fracture healing if malaligned, and nearly two-thirds of patients returned to self-reported baseline function within 1 year.
Level of evidence: Level III, therapeutic study. See Guidelines for Authors for a complete description of levels of evidence.
Figures
References
-
- Black DM, Cummings SR, Karpf DB, Cauley JA, Thompson DE, Nevitt MC, Bauer DC, Genant HK, Haskell WL, Marcus R, Ott SM, Torner JC, Quandt SA, Reiss TF, Ensrud KE. Randomised trial of effect of alendronate on risk of fracture in women with existing vertebral fractures. Fracture Intervention Trial Research Group. Lancet. 1996;348:1535–1541. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)07088-2. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

