Neurochemical characterization of neurons expressing melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 in the mouse hypothalamus
- PMID: 23605441
- PMCID: PMC3633152
- DOI: 10.1002/cne.23273
Neurochemical characterization of neurons expressing melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 in the mouse hypothalamus
Abstract
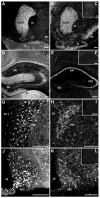
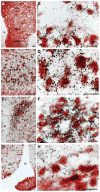
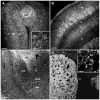
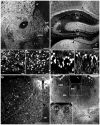
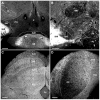
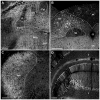
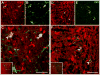
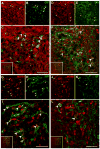
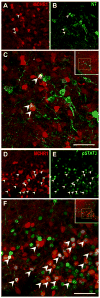
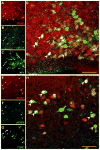
Melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) is a hypothalamic neuropeptide that acts via MCH receptor 1 (MCHR1) in the mouse. It promotes positive energy balance; thus, mice lacking MCH or MCHR1 are lean, hyperactive, and resistant to diet-induced obesity. Identifying the cellular targets of MCH is an important step to understanding the mechanisms underlying MCH actions. We generated the Mchr1-cre mouse that expresses cre recombinase driven by the MCHR1 promoter and crossed it with a tdTomato reporter mouse. The resulting Mchr1-cre/tdTomato progeny expressed easily detectable tdTomato fluorescence in MCHR1 neurons, which were found throughout the olfactory system, striatum, and hypothalamus. To chemically identify MCH-targeted cell populations that play a role in energy balance, MCHR1 hypothalamic neurons were characterized by colabeling select hypothalamic neuropeptides with tdTomato fluorescence. TdTomato fluorescence colocalized with dynorphin, oxytocin, vasopressin, enkephalin, thyrothropin-releasing hormone, and corticotropin-releasing factor immunoreactive cells in the paraventricular nucleus. In the lateral hypothalamus, neurotensin, but neither orexin nor MCH neurons, expressed tdTomato. In the arcuate nucleus, both Neuropeptide Y and proopiomelanocortin cells expressed tdTomato. We further demonstrated that some of these arcuate neurons were also targets of leptin action. Interestingly, MCHR1 was expressed in the vast majority of leptin-sensitive proopiomelanocortin neurons, highlighting their importance for the orexigenic actions of MCH. Taken together, this study supports the use of the Mchr1-cre mouse for outlining the neuroanatomical distribution and neurochemical phenotype of MCHR1 neurons.
Copyright © 2012 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no known or potential conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Abbott CR, Kennedy AR, Wren AM, Rossi M, Murphy KG, Seal LJ, Todd JF, Ghatei MA, Small CJ, Bloom SR. Identification of hypothalamic nuclei involved in the orexigenic effect of melanin-concentrating hormone. Endocrinology. 2003;144:3943–3949. - PubMed
-
- Ahima RS, Prabakaran D, Mantzoros C, Qu D, Lowell B, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS. Role of leptin in the neuroendocrine response to fasting. Nature. 1996;382:250–252. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

