In vivo MRI cell tracking using perfluorocarbon probes and fluorine-19 detection
- PMID: 23606473
- PMCID: PMC3893103
- DOI: 10.1002/nbm.2948
In vivo MRI cell tracking using perfluorocarbon probes and fluorine-19 detection
Abstract
This article presents a brief review of preclinical in vivo cell-tracking methods and applications using perfluorocarbon (PFC) probes and fluorine-19 ((19) F) MRI detection. Detection of the (19) F signal offers high cell specificity and quantification ability in spin density-weighted MR images. We discuss the compositions of matter, methods and applications of PFC-based cell tracking using ex vivo and in situ PFC labeling in preclinical studies of inflammation and cellular therapeutics. We also address the potential applicability of (19) F cell tracking to clinical trials.
Copyright © 2013 John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
Figures
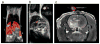
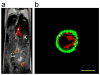
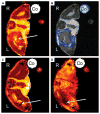
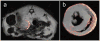


References
-
- Srinivas M, Morel PA, Ernst LA, Laidlaw DH, Ahrens ET. Fluorine-19 MRI for visualization and quantification of cell migration in a diabetes model. Magn Reson Med. 2007;58(4):725–734. - PubMed
-
- Riess JG. Oxygen carriers (“blood substitutes”) - Raison d’etre, chemistry, and some physiology. Chem Rev. 2001;101(9):2797–2919. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

