The Dectin-2 family of C-type lectin-like receptors: an update
- PMID: 23606632
- PMCID: PMC3631001
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxt006
The Dectin-2 family of C-type lectin-like receptors: an update
Abstract
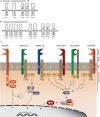
Myeloid and non-myeloid cells express members of the C-type lectin-like receptor (CTLR) family, which mediate crucial cellular functions during immunity and homeostasis. Of relevance here is the dendritic cell-associated C-type lectin-2 (Dectin-2) family of CTLRs, which includes blood dendritic cell antigen 2 (BDCA-2), dendritic cell immunoactivating receptor (DCAR), dendritic cell immunoreceptor (DCIR), Dectin-2, C-type lectin superfamily 8 (CLECSF8) and macrophage-inducible C-type lectin (Mincle). These CTLRs possess a single extracellular conserved C-type lectin-like domain and are capable of mediating intracellular signalling either directly, through integral signalling domains, or indirectly, by associating with signalling adaptor molecules. These receptors recognize a diverse range of endogenous and exogenous ligands, and can function as pattern recognition receptors for several classes of pathogens including fungi, bacteria and parasites, driving both innate and adaptive immunity. In this review, we summarize our knowledge of each of these receptors, highlighting the exciting discoveries that have been made in recent years.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

