The degree of skin involvement identifies distinct lung disease outcomes and survival in systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 23606705
- PMCID: PMC4776325
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202849
The degree of skin involvement identifies distinct lung disease outcomes and survival in systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Objective: To determine whether the pattern of skin involvement can predict clinical features, risk of restrictive lung disease (RLD) and survival in a large scleroderma (SSc) cohort.
Methods: Demographic and clinical data collected over 30 years from 2205 patients with SSc were retrospectively analysed after subdividing subjects into four subtypes based on pattern of skin fibrosis: type 0 (no skin involvement), type 1 (limited to metacarpophalangeal joints), type 2 (distal to elbows/knees) and type 3 (proximal to elbows/knees). Clinical features associated with skin subsets were identified by regression analyses. Kaplan-Meier and Cox proportional hazards models were used to compare time to RLD and survival across subtypes.
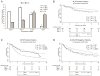
Results: The presence and severity of RLD were positively associated with skin subtype (p<0.001). RLD prevalence incrementally ranged from 51.9% in type 0 to 76.7% in type 3 (p<0.001). Type 2 SSc exhibited a distinct phenotype with intermediate risk for RLD relative to type 1 (higher, p<0.001) and type 3 (lower, p<0.001) and a unique autoantibody profile, with a prevalence of anticentromere antibodies lower than type 1 (28.9% vs 44.1%, p=0.001) and of anti-topoisomerase I antibodies similar to type 3 (32.8% vs 28.7%, p=0.38). These autoantibodies were also found to be significant negative (OR=0.33, p<0.001) and positive (OR=1.6, p=0.01) predictors of RLD risk, respectively. Mortality was also intermediate in type 2 patients relative to type 3 (p=0.0003) and type 1 (p=0.066).
Conclusions: These data suggest that the current classification subdividing SSc into limited and diffuse cutaneous subtypes misclassifies an intermediate group of patients exhibiting unique autoantibody profile, disease course and clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Autoantibodies; Pulmonary Fibrosis; Systemic Sclerosis.
Figures
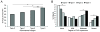


References
-
- Boin F, Wigley FM. Clinical Features and Treatment of Scleroderma. In: Firestein GS, Budd RC, Gabriel SE, McInnes IB, O'Dell JR, editors. Kelley's Textbook of Rheumatology, 9th Edition. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; pp. 2012pp. 1366–1403.
-
- Masi AT, Rodnan GP, Medsger TA, et al. Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma) Subcommittee for scleroderma criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee Arthritis Rheum. 1980;23:581–590. - PubMed
-
- Barnett AJ. Classification of Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma) In: Black CM, Myers AR, editors. Current Topics in Rheumatology: Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma) Vol. 1985. New York, NY: Gower Medical Publishing; p. 18.
-
- Giordano M, Valentini G, Migliaresi S, et al. Different antibody patterns and different prognoses in patients with scleroderma with various extent of skin sclerosis. J Rheumatol. 1986;13:911–916. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

