Innate immunity and its regulation by mast cells
- PMID: 23606723
- PMCID: PMC3645001
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1203420
Innate immunity and its regulation by mast cells
Abstract
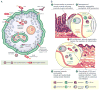
Mast cells (MCs), which are granulated tissue-resident cells of hematopoietic lineage, constitute a major sensory arm of the innate immune system. In this review we discuss the evidence supporting the dual role of MCs, both as sentinels for invading pathogens and as regulatory cells throughout the course of acute inflammation, from its initiation to resolution. This versatility is dependent on the ability of MCs to detect pathogens and danger signals and release a unique panel of mediators to promote pathogen-specific clearance mechanisms, such as through cellular recruitment or vascular permeability. It is increasingly understood that MCs also contribute to the regulated contraction of immune activation that occurs within tissues as inflammation resolves. This overarching regulatory control over innate immune processes has made MCs successful targets to purposefully enhance or, alternatively, suppress MC responses in multiple therapeutic contexts.
Figures
References
-
- Meylan E, Tschopp J, Karin M. Intracellular pattern recognition receptors in the host response. Nature. 2006;442:39–44. - PubMed
-
- Kawai T, Akira S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: update on Toll-like receptors. Nature immunology. 2010;11:373–384. - PubMed
-
- Thoma-Uszynski S, Stenger S, Takeuchi O, Ochoa MT, Engele M, Sieling PA, Barnes PF, Rollinghoff M, Bolcskei PL, Wagner M, Akira S, Norgard MV, Belisle JT, Godowski PJ, Bloom BR, Modlin RL. Induction of direct antimicrobial activity through mammalian toll-like receptors. Science. 2001;291:1544–1547. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R37 DK050814/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AI096305/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01-AI082107/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI082107/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R56-DK095198/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL112921/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK095198/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK101456/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK077159/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DK077307/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R21 DA029731/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI096305/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

