Assessment of hepatic and pancreatic iron overload in pediatric Beta-thalassemic major patients by t2* weighted gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging
- PMID: 23606980
- PMCID: PMC3625578
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/496985
Assessment of hepatic and pancreatic iron overload in pediatric Beta-thalassemic major patients by t2* weighted gradient echo magnetic resonance imaging
Abstract
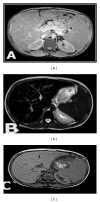
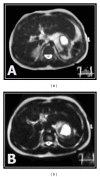
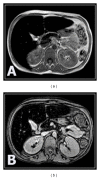
Background. MRI has emerged for the noninvasive assessment of iron overload in various tissues. The aim of this paper is to evaluate hepatic and pancreatic iron overload by T2(∗) weighted gradient echo MRI in young beta-thalassemia major patients and to correlate it with glucose disturbance and postsplenectomy status. Subjects and Methods. 50 thalassemic patients, in addition to 15 healthy controls. All patients underwent clinical assessment and laboratory investigations. Out of 50 thalassemic patients, 37 patients were splenectomized. MRI was performed for all subjects. Results. All patients showed significant reduction in the signal intensity of the liver and the pancreas on T2(∗)GRD compared to controls, thalassemic patients who had abnormal glucose tolerance; diabetic and impaired glucose tolerance patients displayed a higher degree of pancreatic and hepatic siderosis and more T2(∗) drop in their signal intensity than those with normal blood sugar level. Splenectomized thalassemic patients had significantly lower signal intensity of the liver and pancreas compared to nonsplenectomized patients. Conclusion. T2(∗) gradient echo MRI is noninvasive highly sensitive method in assessing hepatic and pancreatic iron overload in thalassemic patients, more evident in patients with abnormal glucose tolerance, and is accelerated in thalassemic splenectomized patients.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

