Treatment of nonhealing diabetic lower extremity ulcers with skin graft and autologous platelet gel: a case series
- PMID: 23607097
- PMCID: PMC3626385
- DOI: 10.1155/2013/837620
Treatment of nonhealing diabetic lower extremity ulcers with skin graft and autologous platelet gel: a case series
Abstract
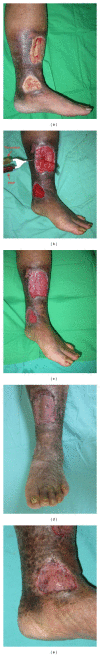
Lower extremity ulcers in diabetic patients are difficult to treat. Recently, the use of human blood platelet-derived components in this indication has been raising interest. In this study, we have evaluated the safety and efficacy of the combination of autologous platelet gel (PG) and skin graft for treating large size recalcitrant ulcers. Eight consecutive diabetic patients aged 25 to 82 with nine nonhealing lower extremity ulcers (median size of 50 cm(2); range 15-150 cm(2)) were treated. Skin ulcer was debrided, and the wound was sprayed after 7 to 10 days with autologous platelet-rich plasma and thrombin. Thin split-thickness skin graft with multiple slits was then applied on the wound bed and fixed with staples or cat-gut sutures. There were no adverse reactions observed during the study. Eight out of 9 skin grafts took well. The interval between skin graft and complete wound healing ranged from 2 to 3 weeks in the 8 successful cases. No ulcer recurrence was noted in those patients during the follow-up period of 2 to 19 months. In this study, the combination of autologous platelet gel and skin grafting has proven beneficial to heal large-size recalcitrant ulcers.
Figures




References
-
- Willrich A, Pinzur M, McNeil M, Juknelis D, Lavery L. Health related quality of life, cognitive function, and depression in diabetic patients with foot ulcer or amputation. A preliminary study. Foot and Ankle International. 2005;26(2):128–134. - PubMed
-
- Apelqvist J, Ragnarson-Tennvall G, Persson U, Larsson J. Diabetic foot ulcers in a multidisciplinary setting. An economic analysis of primary healing and healing with amputation. Journal of Internal Medicine. 1994;235(5):463–471. - PubMed
-
- Loot MA, Kenter SB, Au FL, et al. Fibroblasts derived from chronic diabetic ulcers differ in their response to stimulation with EGF, IGF-I, bFGF and PDGF-AB compared to controls. European Journal of Cell Biology. 2002;81(3):153–160. - PubMed
-
- Steed DL. Clinical evaluation of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor for the treatment of lower extremity ulcers. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2006;117(7, supplement):143S–149S. - PubMed
-
- Steed DL. Clinical evaluation of recombinant human platelet-derived growth factor for the treatment of lower extremity diabetic ulcers. Diabetic Ulcer Study Group. Journal of Vascular Surgery. 1995;21(1):71–78. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

