Delayed onset of graft-versus-host disease in immunodeficent human leucocyte antigen-DQ8 transgenic, murine major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice repopulated by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
- PMID: 23607364
- PMCID: PMC3722935
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12121
Delayed onset of graft-versus-host disease in immunodeficent human leucocyte antigen-DQ8 transgenic, murine major histocompatibility complex class II-deficient mice repopulated by human peripheral blood mononuclear cells
Abstract
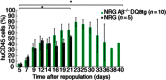
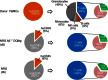
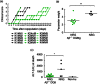
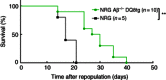
Haematopoietic humanization of mice is used frequently to study the human immune system and its reaction upon experimental intervention. Immunocompromised non-obese diabetic (NOD)-Rag1(-/-) mice, additionally deficient for the common gamma chain of cytokine receptors (γc) (NOD-Rag1(-/-) γc(-/-) mice), lack B, T and natural killer (NK) cells and allow for efficient human peripheral mononuclear cell (PBMC) engraftment. However, a major experimental drawback for studies using these mice is the rapid onset of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). In order to elucidate the contribution of the xenogenic murine major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II in this context, we generated immunodeficient mice expressing human MHC class II [human leucocyte antigen (HLA)-DQ8] on a mouse class II-deficient background (Aβ(-/-) ). We studied repopulation and onset of GVHD in these mouse strains following transplantation of DQ8 haplotype-matched human PBMCs. The presence of HLA class II promoted the repopulation rates significantly in these mice. Virtually all the engrafted cells were CD3(+) T cells. The presence of HLA class II did not advance B cell engraftment, such that humoral immune responses were undetectable. However, the overall survival of DQ8-expressing mice was prolonged significantly compared to mice expressing mouse MHC class II molecules, and correlated with an increased time span until onset of GVHD. Our data thus demonstrate that this new mouse strain is useful to study GVHD, and the prolonged animal survival and engraftment rates make it superior for experimental intervention following PBMC engraftment.
Keywords: MHC class II; graft-versus-host disease (GVHD); immunodeficiency-primary.
© 2013 British Society for Immunology.
Figures


References
-
- Bosma GC, Custer RP, Bosma MJ. A severe combined immunodeficiency mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1983;301:527–530. - PubMed
-
- Lapidot T, Pflumio F, Doedens M, Murdoch B, Williams DE, Dick JE. Cytokine stimulation of multilineage hematopoiesis from immature human cells engrafted in SCID mice. Science. 1992;255:1137–1141. - PubMed
-
- Mosier DE, Gulizia RJ, Baird SM, Wilson DB. Transfer of a functional human immune system to mice with severe combined immunodeficiency. Nature. 1988;335:256–259. - PubMed
-
- Lieber MR, Hesse JE, Lewis S, et al. The defect in murine severe combined immune deficiency: joining of signal sequences but not coding segments in V(D)J recombination. Cell. 1988;55:7–16. - PubMed
-
- Blunt T, Finnie NJ, Taccioli GE, et al. Defective DNA-dependent protein kinase activity is linked to V(D)J recombination and DNA repair defects associated with the murine scid mutation. Cell. 1995;80:813–823. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

