Aberrant expression of microRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis contributes to the immunopathogenesis
- PMID: 23607629
- PMCID: PMC3694534
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12089
Aberrant expression of microRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis contributes to the immunopathogenesis
Abstract
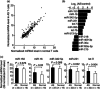
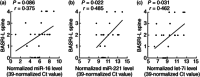
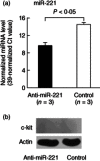
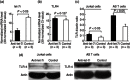
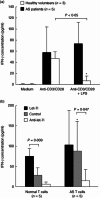
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a chronic inflammatory disorder characterized by dysregulated T cells. We hypothesized that the aberrant expression of microRNAs (miRNAs) in AS T cells involved in the pathogenesis of AS. The expression profile of 270 miRNAs in T cells from five AS patients and five healthy controls were analysed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Thirteen miRNAs were found potentially differential expression. After validation, we confirmed that miR-16, miR-221 and let-7i were over-expressed in AS T cells and the expression of miR-221 and let-7i were correlated positively with the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI) of lumbar spine in AS patients. The protein molecules regulated by miR-16, miR-221 and let-7i were measured by Western blotting. We found that the protein levels of Toll-like receptor-4 (TLR-4), a target of let-7i, in T cells from AS patients were decreased. In addition, the mRNA expression of interferon (IFN)-γ was elevated in AS T cells. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a TLR-4 agonist, inhibited IFN-γ secretion by anti-CD3(+) anti-CD28 antibodies-stimulated normal T cells but not AS T cells. In the transfection studies, we found the increased expression of let-7i enhanced IFN-γ production by anti-CD3(+) anti-CD28(+) lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated normal T cells. In contrast, the decreased expression of let-7i suppressed IFN-γ production by anti-CD3(+) anti-CD28(+) LPS-stimulated AS T cells. In conclusion, we found that miR-16, miR-221 and let-7i were over-expressed in AS T cells, but only miR-221 and let-7i were associated with BASRI of lumbar spine. In the functional studies, the increased let-7i expression facilitated the T helper type 1 (IFN-γ) immune response in T cells.
© 2013 British Society for Immunology.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The Role of MicroRNAS in Ankylosing Spondylitis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(14):e3325. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003325. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27057910 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Let-7i Regulates Innate TLR4 Pathways in Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells of Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Apr 19;16:1393-1401. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S397160. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37155468 Free PMC article.
-
Increased miR-223 expression in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis leads to decreased insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated interleukin-10 production.Clin Exp Immunol. 2014 Sep;177(3):641-51. doi: 10.1111/cei.12374. Clin Exp Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24816316 Free PMC article.
-
Aberrant expression of interleukin-23-regulated miRNAs in T cells from patients with ankylosing spondylitis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2018 Nov 21;20(1):259. doi: 10.1186/s13075-018-1754-1. Arthritis Res Ther. 2018. PMID: 30463609 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs dysregulation in ankylosing spondylitis: A review of implications for disease mechanisms, and diagnostic markers.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 May;268(Pt 2):131814. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.131814. Epub 2024 Apr 26. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38677679 Review.
Cited by
-
Serum miRNA Signature in Rheumatoid Arthritis and "At-Risk Individuals".Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 3;12:633201. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.633201. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33746971 Free PMC article.
-
miR-573 is a negative regulator in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis.Cell Mol Immunol. 2016 Nov;13(6):839-849. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2015.63. Epub 2015 Jul 13. Cell Mol Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26166764 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Pathogenesis of Ankylosing Spondylitis.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Jul 7;2019:6920281. doi: 10.1155/2019/6920281. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 31360722 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of mRNA Modifications in Bone Diseases.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jan 13;21(3):1065-1080. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.104460. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39897026 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MicroRNAS in Ankylosing Spondylitis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2016 Apr;95(14):e3325. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000003325. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016. PMID: 27057910 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

