Positive immunostaining for feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) in a Sphinx cat with cutaneous lesions and bilateral panuveitis
- PMID: 23607772
- PMCID: PMC7169334
- DOI: 10.1111/vop.12044
Positive immunostaining for feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) in a Sphinx cat with cutaneous lesions and bilateral panuveitis
Abstract
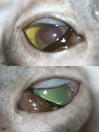
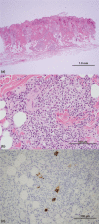
Feline infectious peritonitis (FIP) is a common, fatal, systemic disease of cats. This case report describes the antemortem diagnosis of FIP in a 2-year-old spayed female Sphinx cat that presented with a bilateral panuveitis and multiple papular cutaneous lesions. Histopathologically, the skin lesions were characterized by perivascular infiltrates of macrophages, neutrophils, with fewer plasma cells, mast cells, and small lymphocytes in the mid- to deep dermis. Immunohistochemistry for intracellular feline coronavirus (FeCoV) antigen demonstrated positive staining in dermal macrophages providing an antemortem diagnosis of a moderate, nodular to diffuse, pyogranulomatous perivascular dermatitis due to FIP infection. Obtaining an antemortem diagnosis of FIP can be a challenge and cutaneous lesions are rare in the disease. Recognition and biopsy of any cutaneous lesions in cats with panuveitis and suspected FIP can help establish an antemortem diagnosis of the disease.
Keywords: feline infectious peritonitis; immunohistochemistry; panuveitis; skin.
© 2013 American College of Veterinary Ophthalmologists.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

