Does atlantoaxial dislocation influence the subaxial cervical spine?
- PMID: 23608933
- PMCID: PMC3698338
- DOI: 10.1007/s00586-013-2742-4
Does atlantoaxial dislocation influence the subaxial cervical spine?
Abstract
Introduction: Previous studies have reported that the alignments of the occipital-cervical and subaxial spine were closely interrelated in asymptomatic individuals; however, none have focused on a population with atlantoaxial dislocation.
Material and methods: From 2007 to 2011, 298 patients with atlantoaxial dislocation and atlas occipitalization were studied. Angles formed between Occiput-C2 and C2-C7 were measured. The relationship between the alignment of the occipital-cervical junction and the subaxial cervical spine was evaluated.
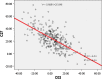
Results: The range of values for the angles measured was as followed: the Occiput-C2 angles were -35.2° to 44.8°, and the C2-C7 angles were -17.4° to 77.8°. Statistically significant negative correlations were observed between the Occiput-C2 and C2-C7 angles.
Conclusion: Anterior dislocations of the atlas are associated with diminished lordosis or even kyphosis of the occipital-cervical junction, and result in compensatory hyperlordosis of the subaxial cervical spine, collectively presenting as a "swan neck" deformity. Atlantoaxial dislocation may influence the global cervical alignment.
Figures


References
-
- Clark C, Goetz D, Menezes A. Arthrodesis of the cervical spine in rheumatoid arthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1989;71:381–392. - PubMed
-
- Goto S, Mochizuki M, Kita T, Murakami M, Nishigaki H, Moriya H. Transoral joint release of the dislocated atlantoaxial joints combined with posterior reduction and fusion for a late infantile atlantoaxial rotatory fixation. A case report. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 1998;23:1485–1489. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199807010-00010. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

