Effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding on branched-chain amino acid metabolism
- PMID: 23610059
- PMCID: PMC3717831
- DOI: 10.2337/db13-0185
Effect of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding on branched-chain amino acid metabolism
Abstract
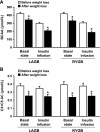
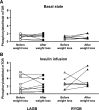
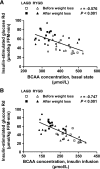
It has been hypothesized that a greater decline in circulating branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs) after weight loss induced by Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery than after calorie restriction alone has independent effects on glucose homeostasis, possibly by decreased signaling through the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). We evaluated plasma BCAAs and their C3 and C5 acylcarnitine metabolites, muscle mTOR phosphorylation, and insulin sensitivity (insulin-stimulated glucose Rd) in obese subjects before and after ~20% weight loss induced by RYGB (n = 10, BMI 45.6 ± 6.7 kg/m(2)) or laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding (LAGB) (n = 10, BMI 46.5 ± 8.8 kg/m(2)). Weight loss increased insulin-stimulated glucose Rd by ~55%, decreased total plasma BCAA and C3 and C5 acylcarnitine concentrations by 20-35%, and did not alter mTOR phosphorylation; no differences were detected between surgical groups (all P values for interaction >0.05). Insulin-stimulated glucose Rd correlated negatively with plasma BCAAs and with C3 and C5 acylcarnitine concentrations (r values -0.56 to -0.75, P < 0.05). These data demonstrate that weight loss induced by either LAGB or RYGB causes the same decline in circulating BCAAs and their C3 and C5 acylcarnitine metabolites. Plasma BCAA concentration is negatively associated with skeletal muscle insulin sensitivity, but the mechanism(s) responsible for this relationship is not known.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00981500.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- T32 HL007456/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DK 37948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK58398/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK037948/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK058398/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- RR-00954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK 56341/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P41 RR000954/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

