ShortStack: comprehensive annotation and quantification of small RNA genes
- PMID: 23610128
- PMCID: PMC3683909
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.035279.112
ShortStack: comprehensive annotation and quantification of small RNA genes
Abstract
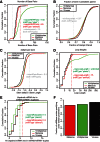
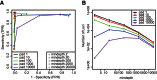
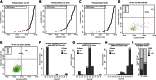
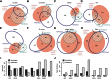
Small RNA sequencing allows genome-wide discovery, categorization, and quantification of genes producing regulatory small RNAs. Many tools have been described for annotation and quantification of microRNA loci (MIRNAs) from small RNA-seq data. However, in many organisms and tissue types, MIRNA genes comprise only a small fraction of all small RNA-producing genes. ShortStack is a stand-alone application that analyzes reference-aligned small RNA-seq data and performs comprehensive de novo annotation and quantification of the inferred small RNA genes. ShortStack's output reports multiple parameters of direct relevance to small RNA gene annotation, including RNA size distributions, repetitiveness, strandedness, hairpin-association, MIRNA annotation, and phasing. In this study, ShortStack is demonstrated to perform accurate annotations and useful descriptions of diverse small RNA genes from four plants (Arabidopsis, tomato, rice, and maize) and three animals (Drosophila, mice, and humans). ShortStack efficiently processes very large small RNA-seq data sets using modest computational resources, and its performance compares favorably to previously described tools. Annotation of MIRNA loci by ShortStack is highly specific in both plants and animals. ShortStack is freely available under a GNU General Public License.
Keywords: bioinformatics; microRNA; next-generation sequencing; siRNA; small RNA; software.
Figures


References
-
- Allen E, Xie Z, Gustafson AM, Carrington JC 2005. microRNA-directed phasing during trans-acting siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 121: 207–221 - PubMed
-
- Aravin A, Gaidatzis D, Pfeffer S, Lagos-Quintana M, Landgraf P, Iovino N, Morris P, Brownstein MJ, Kuramochi-Miyagawa S, Nakano T, et al. 2006. A novel class of small RNAs binds to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature 442: 203–207 - PubMed
-
- Brennecke J, Aravin AA, Stark A, Dus M, Kellis M, Sachidanandam R, Hannon GJ 2007. Discrete small RNA-generating loci as master regulators of transposon activity in Drosophila. Cell 128: 1089–1103 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
