A multi-layer inference approach to reconstruct condition-specific genes and their regulation
- PMID: 23610368
- PMCID: PMC3673221
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btt186
A multi-layer inference approach to reconstruct condition-specific genes and their regulation
Abstract
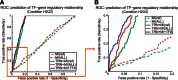
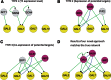
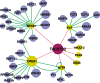
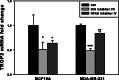
An important topic in systems biology is the reverse engineering of regulatory mechanisms through reconstruction of context-dependent gene networks. A major challenge is to identify the genes and the regulations specific to a condition or phenotype, given that regulatory processes are highly connected such that a specific response is typically accompanied by numerous collateral effects. In this study, we design a multi-layer approach that is able to reconstruct condition-specific genes and their regulation through an integrative analysis of large-scale information of gene expression, protein interaction and transcriptional regulation (transcription factor-target gene relationships). We establish the accuracy of our methodology against synthetic datasets, as well as a yeast dataset. We then extend the framework to the application of higher eukaryotic systems, including human breast cancer and Arabidopsis thaliana cold acclimation. Our study identified TACSTD2 (TROP2) as a target gene for human breast cancer and discovered its regulation by transcription factors CREB, as well as NFkB. We also predict KIF2C is a target gene for ER-/HER2- breast cancer and is positively regulated by E2F1. The predictions were further confirmed through experimental studies.
Availability: The implementation and detailed protocol of the layer approach is available at http://www.egr.msu.edu/changroup/Protocols/Three-layer%20approach%20 to % 20reconstruct%20condition.html.
Figures


References
-
- Abdel-Fatah T, et al. P4-09-11: kinesin family member 2C (KIF2C) is a new surrogate prognostic marker in breast cancer (BC) Cancer Res. 2012;71:P4–09–11.
-
- Agarwal M, et al. A R2R3 type MYB transcription factor is involved in the cold regulation of CBF genes and in acquired freezing tolerance. J. Biol. Chem. 2006;281:37636–37645. - PubMed
-
- Almuallim H, Dietterich TG. Proceedings of The Ninth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Menlo Park, CA: AAAI Press; 1991. Learning with many irrelevant features; pp. 547–552.
-
- Basso K, et al. Reverse engineering of regulatory networks in human B cells. Nat. Genet. 2005;37:382–390. - PubMed
-
- Bontempi G, Meyer PE. Causal filter selection in microarray data. ICML. 2010:95–102.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

