Holo-TFIID controls the magnitude of a transcription burst and fine-tuning of transcription
- PMID: 23610421
- PMCID: PMC3651496
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1221712110
Holo-TFIID controls the magnitude of a transcription burst and fine-tuning of transcription
Abstract
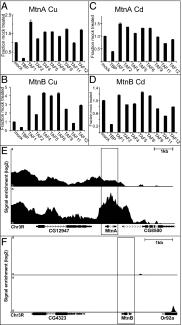
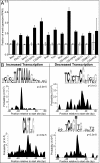
Transcription factor (TF)IID is a central player in activated transcription initiation. Recent evidence suggests that the role and composition of TFIID are more diverse than previously understood. To investigate the effects of changing the composition of TFIID in a simple system, we depleted TATA box-binding protein-associated factor (TAF)1 from Drosophila cells and determined the consequences on metal-induced transcription at an inducible gene, metallothionein B. We observe a marked increase in the levels of both the mature message and pre-mRNA in TAF1-depleted cells. Under conditions of continued metal exposure, we show that TAF1 depletion increases the magnitude of the initial transcription burst but has no effect on the timing of that burst. We also show that TAF1 depletion causes delay in the shutoff of transcription upon removal of the stimulus. Thus, TAFs are involved in both establishing an upper limit of transcription during induction and efficiently turning the gene off once the inducer is removed. Using genome-wide nascent sequencing, we identify hundreds of genes that are controlled in a similar manner, indicating that the findings at this inducible gene are likely generalizable to a large set of promoters. There is a long-standing appreciation for the importance of the spatial and temporal control of transcription. Here we uncover an important third dimension of control: the magnitude of the response. Our results show that the magnitude of the transcriptional response to the same signaling event, even at the same promoter, can vary greatly depending on the composition of the TFIID complex in the cell.
Keywords: MtnA; RNA polymerase; coactivator; heavy metal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TAF4 nucleates a core subcomplex of TFIID and mediates activated transcription from a TATA-less promoter.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006 Aug 15;103(33):12347-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0605499103. Epub 2006 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006. PMID: 16895980 Free PMC article.
-
Nucleolar colocalization of TAF1 and testis-specific TAFs during Drosophila spermatogenesis.Dev Dyn. 2007 Oct;236(10):2836-43. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.21294. Dev Dyn. 2007. PMID: 17823958
-
DNA binding properties of TAF1 isoforms with two AT-hooks.J Biol Chem. 2006 Oct 6;281(40):30015-23. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M606289200. Epub 2006 Aug 7. J Biol Chem. 2006. PMID: 16893881
-
SAGA and TFIID: Friends of TBP drifting apart.Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021 Feb;1864(2):194604. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2020.194604. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 2021. PMID: 32673655 Review.
-
The roles of TAF1 in neuroscience and beyond.R Soc Open Sci. 2024 Sep 25;11(9):240790. doi: 10.1098/rsos.240790. eCollection 2024 Sep. R Soc Open Sci. 2024. PMID: 39323550 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pluralistic and stochastic gene regulation: examples, models and consistent theory.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Jun 2;44(10):4595-609. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw042. Epub 2016 Jan 28. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26823500 Free PMC article.
-
The Core Promoter Is a Regulatory Hub for Developmental Gene Expression.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Sep 10;9:666508. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.666508. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34568311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Real-time visualization of reconstituted transcription reveals RNA polymerase II activation mechanisms at single promoters.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jan 6:2025.01.06.631569. doi: 10.1101/2025.01.06.631569. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 39829877 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Transcriptional refractoriness is dependent on core promoter architecture.Nat Commun. 2015 Apr 8;6:6753. doi: 10.1038/ncomms7753. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 25851692
-
TFIID Enables RNA Polymerase II Promoter-Proximal Pausing.Mol Cell. 2020 May 21;78(4):785-793.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.03.008. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Mol Cell. 2020. PMID: 32229306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tanese N, Pugh BF, Tjian R. Coactivators for a proline-rich activator purified from the multisubunit human TFIID complex. Genes Dev. 1991;5(12A):2212–2224. - PubMed
-
- Dynlacht BD, Hoey T, Tjian R. Isolation of coactivators associated with the TATA-binding protein that mediate transcriptional activation. Cell. 1991;66(3):563–576. - PubMed
-
- Tora L. A unified nomenclature for TATA box binding protein (TBP)-associated factors (TAFs) involved in RNA polymerase II transcription. Genes Dev. 2002;16(6):673–675. - PubMed
-
- Näär AM, Lemon BD, Tjian R. Transcriptional coactivator complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 2001;70:475–501. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

