Recent Progress in Lab-on-a-Chip Technology and Its Potential Application to Clinical Diagnoses
- PMID: 23610705
- PMCID: PMC3627994
- DOI: 10.5213/inj.2013.17.1.2
Recent Progress in Lab-on-a-Chip Technology and Its Potential Application to Clinical Diagnoses
Abstract
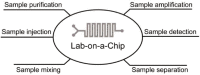
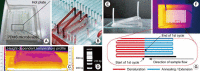
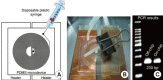
We present the construction of the lab-on-a-chip (LOC) system, a state-of-the-art technology that uses polymer materials (i.e., poly[dimethylsiloxane]) for the miniaturization of conventional laboratory apparatuses, and show the potential use of these microfluidic devices in clinical applications. In particular, we introduce the independent unit components of the LOC system and demonstrate how each component can be functionally integrated into one monolithic system for the realization of a LOC system. In specific, we demonstrate microscale polymerase chain reaction with the use of a single heater, a microscale sample injection device with a disposable plastic syringe and a strategy for device assembly under environmentally mild conditions assisted by surface modification techniques. In this way, we endeavor to construct a totally integrated, disposable microfluidic system operated by a single mode, the pressure, which can be applied on-site with enhanced device portability and disposability and with simple and rapid operation for medical and clinical diagnoses, potentially extending its application to urodynamic studies in molecular level.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Disposable equipment; Lab-on-a-chip devices; Micro-electrical-mechanical systems; Miniaturization; Polymers.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

References
-
- Kricka LJ, Wilding P. Microchip PCR. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2003;377:820–825. - PubMed
-
- Zhang C, Xu J, Ma W, Zheng W. PCR microfluidic devices for DNA amplification. Biotechnol Adv. 2006;24:243–284. - PubMed
-
- Shen K, Chen X, Guo M, Cheng J. A microchip-based PCR device using flexible printed circuit technology. Sens Actuator B. 2005;105:251–258.
-
- Christensen TB, Bang DD, Wolff A. Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) on a SU-8 chip. Microelectron Eng. 2008;85:1278–1281.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

