Is Imaging Time Between two Tc 99m DMSA Scans Sufficient for Reporting as Renal Parenchymal Scarring? Healed Parenchymal Renal Defect After 6 Years
- PMID: 23610726
- PMCID: PMC3629786
- DOI: 10.4274/Mirt.22
Is Imaging Time Between two Tc 99m DMSA Scans Sufficient for Reporting as Renal Parenchymal Scarring? Healed Parenchymal Renal Defect After 6 Years
Abstract
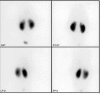
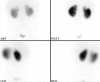
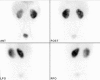
We aimed to report a healed renal parenchymal defect after 6 years in a 9-year-old girl who was being followed for recurrent urinary tract infection (UTI). The first UTI was at the age of two. She was being followed with ultrasonography, urine analysis and urine culture since the first UTI. Technetium-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scintigraphy was repeated four times up to the present day. She had a renal parenchymal defect reported as parenchymal scarring, which healed 6 years after the first DMSA scintigraphy.
Conflict of interest: None declared.
Keywords: Kidney cortex necrosis; technetium Tc-99m dimercaptosuccinic acid; urinary tract infections.
Figures

Similar articles
-
123I-hippuran renal scintigraphy with evaluation of single-kidney clearance for predicting renal scarring after acute urinary tract infection: comparison with (99m)Tc-DMSA scanning.J Nucl Med. 2003 Nov;44(11):1755-60. J Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 14602856
-
Technetium-99m-N,N-ethylenedicysteine and Tc-99m DMSA scintigraphy in the evaluation of renal parenchymal abnormalities in children.Ann Nucl Med. 2003 May;17(3):219-25. doi: 10.1007/BF02990025. Ann Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 12846544 Clinical Trial.
-
Potential utility of MRI in the evaluation of children at risk of renal scarring.Pediatr Radiol. 1999 Nov;29(11):856-62. doi: 10.1007/s002470050713. Pediatr Radiol. 1999. PMID: 10552069
-
Update on dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scanning in children with urinary tract infection.Pediatr Nephrol. 1995 Apr;9(2):221-6; discussion 227. doi: 10.1007/BF00860755. Pediatr Nephrol. 1995. PMID: 7794724 Review.
-
Dimercaptosuccinic acid renal scintigraphy for the evaluation of pyelonephritis and scarring: a review of experimental and clinical studies.J Urol. 1992 Nov;148(5 Pt 2):1726-32. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5347(17)37014-3. J Urol. 1992. PMID: 1331545 Review.
References
-
- Rushton HG. Urinary tract infections in children: epidemiology, evaluation and management. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1997;44:1133–1169. - PubMed
-
- Hoberman A, Chao HP, Keller DM, Hickey R, Davis HW, Ellis D. Prevalence of urinary tract infection in febrile infants. J Pediatr. 1993;123:17–23. - PubMed
-
- Benador D, Benador N, Slosman DO, Nussle D, Mermillod B, Girardin E. Cortical scintigraphy in the evaluation of renal parenchyma changes in children with pyelonephritis. J Pediatr. 1994;124:17–20. - PubMed
-
- Ataei N, Madani A, Habibi R, Khorasani M. Evaluation of acute pyelonephritis with DMSA scans in children presenting after the age of 5 years. Pediatr Nephrol. 2005;20:1439–1444. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
