Gastroprotective effects of Corchorus olitorius leaf extract against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal hemorrhagic lesions in rats
- PMID: 23611708
- PMCID: PMC3842111
- DOI: 10.1111/jgh.12229
Gastroprotective effects of Corchorus olitorius leaf extract against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal hemorrhagic lesions in rats
Retraction in
-
Retraction: Rami Al Batran, Fouad Al-Bayaty, Mahmood Ameen Abdulla, Mazen M Jamil Al-Obaidi, Maryam Hajrezaei, Pouya Hassandarvish, Mustafa Fouad, Shahram Golbabapour, Samaneh Talaee. Gastroprotective effects of Corchorus olitorius. J Gastroenterol Hepatol, 28: 1321-1329. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.12229.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024 Jul;39(7):1450. doi: 10.1111/jgh.16551. Epub 2024 Apr 26. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2024. PMID: 38668687 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background and aim: Corchorus olitorius is a medicinal plant traditionally utilized as an antifertility, anti-convulsive, and purgative agent. This study aimed to evaluate the gastroprotective effect of an ethanolic extract of C. olitorius against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in adult Sprague Dawley rats.
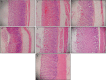
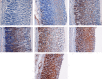
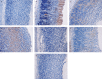
Methods: The rats were divided into seven groups according to their pretreatment: an untreated control group, an ulcer control group, a reference control group (20 mg/kg omeprazole), and four experimental groups (50, 100, 200, or 400 mg/kg of extract). Carboxymethyl cellulose was the vehicle for the agents. Prior to the induction of gastric ulcers with absolute ethanol, the rats in each group were pretreated orally. An hour later, the rats were sacrificed, and gastric tissues were collected to evaluate the ulcers and to measure enzymatic activity. The tissues were subjected to histological and immunohistochemical evaluations.
Results: Compared with the extensive mucosal damage in the ulcer control group, gross evaluation revealed a marked protection of the gastric mucosa in the experimental groups, with significantly preserved gastric wall mucus. In these groups, superoxide dismutase and malondialdehyde levels were significantly increased (P < 0.05) and reduced (P < 0.05), respectively. In addition to the histologic analyses (HE and periodic acid-Schiff staining), immunohistochemistry confirmed the protection through the upregulation of Hsp70 and the downregulation of Bax proteins. The gastroprotection of the experimental groups was comparable to that of the reference control medicine omeprazole.
Conclusions: Our study reports the gastroprotective property of an ethanolic extract of C. olitorius against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal hemorrhagic lesions in rats.
Keywords: Corchorus olitorius; gastric ulcer; gastroprotection; histology; immunohistochemistry.
© 2013 The Authors. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology published by Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology Foundation and Wiley Publishing Asia Pty Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Huang JQ, Sridhar S, Hunt RH. Role of Helicobacter pylori infection and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in peptic-ulcer disease: a meta-analysis. Lancet. 2002;359:14–22. - PubMed
-
- Nakashita M, Suzuki H, Miura S, et al. Attenuation of acetic Acid-induced gastric ulcer formation in rats by glucosylceramide synthase inhibitors. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2013;58:354–362. - PubMed
-
- Kato S, Kawase T, Alderman J, Inatomi N, Lieber CS. Role of xanthine oxidase in ethanol-induced lipid peroxidation in rats. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:203–210. - PubMed
-
- Szabo S, Trier JS, Brown A, Schnoor J. Early vascular injury and increased vascular permeability in gastric mucosal injury caused by ethanol in the rat. Gastroenterology. 1985;88:228–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

