Magnetic barcode assay for genetic detection of pathogens
- PMID: 23612293
- PMCID: PMC3635151
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms2745
Magnetic barcode assay for genetic detection of pathogens
Abstract
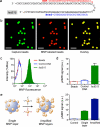
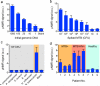
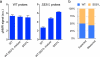
The task of rapidly identifying patients infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis in resource-constrained environments remains a challenge. A sensitive and robust platform that does not require bacterial isolation or culture is critical in making informed diagnostic and therapeutic decisions. Here we introduce a platform for the detection of nucleic acids based on a magnetic barcoding strategy. PCR-amplified mycobacterial genes are sequence-specifically captured on microspheres, labelled by magnetic nanoprobes and detected by nuclear magnetic resonance. All components are integrated into a single, small fluidic cartridge for streamlined on-chip operation. We use this platform to detect M. tuberculosis and identify drug-resistance strains from mechanically processed sputum samples within 2.5 h. The specificity of the assay is confirmed by detecting a panel of clinically relevant non-M. tuberculosis bacteria, and the clinical utility is demonstrated by the measurements in M. tuberculosis-positive patient specimens. Combined with portable systems, the magnetic barcode assay holds promise to become a sensitive, high-throughput and low-cost platform for point-of-care diagnostics.
Figures



References
-
- Kaigala GV, et al. Automated screening using microfluidic chip-based PCR and product detection to assess risk of BK virus-associated nephropathy in renal transplant recipients. Electrophoresis. 2006;27:3753–3763. - PubMed
-
- WHO . Global tuberculosis control: WHO Report. WHO; Geneva: 2012. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 CA079443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB010011/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01-EB010011/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AI007638/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 OD001378/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- T32CA79443/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-EB00462605A1/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- P41 EB002503/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01-HL113156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 0D001378/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- U19 AI076217/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201000044C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 EB004626/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL113156/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

