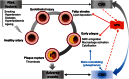
Osteopontin: an emerging therapeutic target in uraemic vascular disease
- PMID: 23612585
- PMCID: PMC3656615
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvt098
Osteopontin: an emerging therapeutic target in uraemic vascular disease
Figures
Comment on
-
Osteopontin deficiency dampens the pro-atherogenic effect of uraemia.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jun 1;98(3):352-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt049. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23455547
Similar articles
-
Osteopontin deficiency dampens the pro-atherogenic effect of uraemia.Cardiovasc Res. 2013 Jun 1;98(3):352-9. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvt049. Epub 2013 Mar 1. Cardiovasc Res. 2013. PMID: 23455547
-
Catch and Release: NG2-Coated Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Capture Lipoproteins for Macrophages.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016 Jan;36(1):7-8. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.115.306798. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26700135 No abstract available.
-
Uremia modulates the phenotype of aortic smooth muscle cells.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Feb;257:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.12.022. Epub 2016 Dec 23. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28107707
-
Vascular smooth muscle cells and monocyte-macrophages accomplice in the accelerated atherosclerosis of insulin resistance states.Cardiovasc Res. 2014 Jul 15;103(2):194-5. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvu144. Epub 2014 Jun 5. Cardiovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 24903495 Review. No abstract available.
-
Role of thrombin in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis.J Cell Biochem. 2019 Apr;120(4):4757-4765. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27771. Epub 2018 Sep 30. J Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30269382 Review.
Cited by
-
Review of the Protective Mechanism of Paeonol on Cardiovascular Disease.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Jul 26;17:2193-2208. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S414752. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37525853 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibiting vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation mediated by osteopontin via regulating gut microbial lipopolysaccharide: A novel mechanism for paeonol in atherosclerosis treatment.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 11;13:936677. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.936677. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36034838 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac function in renovascular hypertensive patients with and without renal dysfunction.Am J Hypertens. 2014 Mar;27(3):445-53. doi: 10.1093/ajh/hpt203. Epub 2013 Oct 25. Am J Hypertens. 2014. PMID: 24162729 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bethesda, MD: National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases; 2011. U.S. Renal Data System, USRDS 2011 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease and End-Stage Renal Disease in the United States.
-
- London GM, Guerin AP, Marchais SJ, Metivier F, Pannier B, Adda H. Arterial media calcification in end-stage renal disease: impact on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003;18:1731–1740. - PubMed
-
- Moe SM, Chen NX. Mechanisms of vascular calcification in chronic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2008;19:213–216. - PubMed
-
- Baber U, de Lemos JA, Khera A, McGuire DK, Omland T, Toto RD, et al. Non-traditional risk factors predict coronary calcification in chronic kidney disease in a population-based cohort. Kidney Int. 2008;73:615–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials