Apolipoprotein E levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of north Indian patients with Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 23612909
- PMCID: PMC10852682
- DOI: 10.1177/1533317513481097
Apolipoprotein E levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of north Indian patients with Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
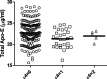
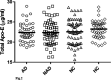
The etiology of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is multifactorial involving both genetic and environmental factors. Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) gene plays a pivotal role in risk and age of onset of AD. Although it is broadly accepted that ApoE genotype is linked to the pathogenesis of AD, there are still controversial results regarding the association of ApoE levels in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) with the occurrence of AD. Some studies have shown a positive correlation between CSF ApoE levels and AD, whereas others showed no link. In this study, we measured ApoE levels to assess the usefulness of CSF ApoE as a diagnostic marker of AD by comparing the levels in 3 patient groups and in control participants. No significant difference was observed in CSF ApoE concentrations between the patients with AD and the controls. So, it appears that CSF ApoE measurement does not offer any diagnostic advantage for AD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer's disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2008;4(2):110–133. - PubMed
-
- Ashford JW, Mortimer JA. Non-familial Alzheimer's disease is mainly due to genetic factors. J Alzheimers Dis. 2002;4(3):169–177. - PubMed
-
- Panza F, Solfrizzi V, D'Introno A, et al. Genetics of late-onset Alzheimer's disease: vascular risk and beta-amyloid metabolism [article in Italian]. Recenti Prog Med. 2002;93(9):489–497. - PubMed
-
- Raber J, Huang Y, Ashford JW. ApoE genotype accounts for the vast majority of AD risk and AD pathology. Neurobiol Aging. 2004;25(5):641–650. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

