Batroxobin binds fibrin with higher affinity and promotes clot expansion to a greater extent than thrombin
- PMID: 23612970
- PMCID: PMC3675619
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.464750
Batroxobin binds fibrin with higher affinity and promotes clot expansion to a greater extent than thrombin
Abstract
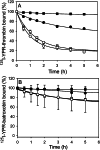
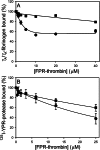
Batroxobin is a thrombin-like serine protease from the venom of Bothrops atrox moojeni that clots fibrinogen. In contrast to thrombin, which releases fibrinopeptide A and B from the NH2-terminal domains of the Aα- and Bβ-chains of fibrinogen, respectively, batroxobin only releases fibrinopeptide A. Because the mechanism responsible for these differences is unknown, we compared the interactions of batroxobin and thrombin with the predominant γA/γA isoform of fibrin(ogen) and the γA/γ' variant with an extended γ-chain. Thrombin binds to the γ'-chain and forms a higher affinity interaction with γA/γ'-fibrin(ogen) than γA/γA-fibrin(ogen). In contrast, batroxobin binds both fibrin(ogen) isoforms with similar high affinity (Kd values of about 0.5 μM) even though it does not interact with the γ'-chain. The batroxobin-binding sites on fibrin(ogen) only partially overlap with those of thrombin because thrombin attenuates, but does not abrogate, the interaction of γA/γA-fibrinogen with batroxobin. Furthermore, although both thrombin and batroxobin bind to the central E-region of fibrinogen with a Kd value of 2-5 μM, the α(17-51) and Bβ(1-42) regions bind thrombin but not batroxobin. Once bound to fibrin, the capacity of batroxobin to promote fibrin accretion is 18-fold greater than that of thrombin, a finding that may explain the microvascular thrombosis that complicates envenomation by B. atrox moojeni. Therefore, batroxobin binds fibrin(ogen) in a manner distinct from thrombin, which may contribute to its higher affinity interaction, selective fibrinopeptide A release, and prothrombotic properties.
Keywords: Batroxobin; Blood Coagulation Factors; Fibrin; Fibrinogen; Fibrinopeptides; Snake Venom; Thrombin.
Figures






References
-
- Wolberg A. S. (2012) Determinants of fibrin formation, structure, and function. Curr. Opin. Hematol. 19, 349–356 - PubMed
-
- Mosesson M. W. (2005) Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 3, 1894–1904 - PubMed
-
- Chung D. W., Davie E. W. (1984) γ and γ′ chains of human fibrinogen are produced by alternative mRNA processing. Biochemistry 23, 4232–4236 - PubMed
-
- Fornace A. J., Jr., Cummings D. E., Comeau C. M., Kant J. A., Crabtree G. R. (1984) Structure of the human γ-fibrinogen gene. Alternate mRNA splicing near the 3′ end of the gene produces γA and γB forms of γ-fibrinogen. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 12826–12830 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

