Down-regulation of wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1) plays a critical role in regulating several p53-dependent functions in premature senescent tumor cells
- PMID: 23612976
- PMCID: PMC3675561
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M112.435149
Down-regulation of wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1) plays a critical role in regulating several p53-dependent functions in premature senescent tumor cells
Abstract
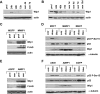
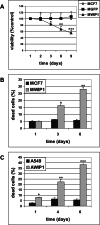
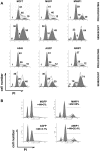
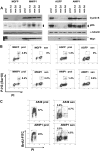
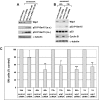
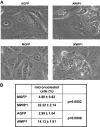
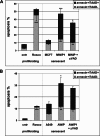
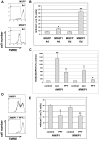
Premature or drug-induced senescence is a major cellular response to chemotherapy in solid tumors. The senescent phenotype develops slowly and is associated with chronic DNA damage response. We found that expression of wild-type p53-induced phosphatase 1 (Wip1) is markedly down-regulated during persistent DNA damage and after drug release during the acquisition of the senescent phenotype in carcinoma cells. We demonstrate that down-regulation of Wip1 is required for maintenance of permanent G2 arrest. In fact, we show that forced expression of Wip1 in premature senescent tumor cells induces inappropriate re-initiation of mitosis, uncontrolled polyploid progression, and cell death by mitotic failure. Most of the effects of Wip1 may be attributed to its ability to dephosphorylate p53 at Ser(15) and to inhibit DNA damage response. However, we also uncover a regulatory pathway whereby suppression of p53 Ser(15) phosphorylation is associated with enhanced phosphorylation at Ser(46), increased p53 protein levels, and induction of Noxa expression. On the whole, our data indicate that down-regulation of Wip1 expression during premature senescence plays a pivotal role in regulating several p53-dependent aspects of the senescent phenotype.
Keywords: Cancer; Cell Death; Cellular Senescence; DNA Damage Response; Polyploidy; Wip1; p53.
Figures

References
-
- Hayflick L., Moorhead P. S. (1961) The serial cultivation of human diploid cell strains. Exp. Cell Res. 25, 585–621 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Blandino G., Oren M., Givol D. (1998) Induced p53 expression in lung cancer cell line promotes cell senescence and differentially modifies the cytotoxicity of anti-cancer drugs. Oncogene 17, 1923–1930 - PubMed
-
- Wang Y., Blandino G., Givol D. (1999) Induced p21waf expression in H1299 cell line promotes cell senescence and protects against cytotoxic effect of radiation and doxorubicin. Oncogene 18, 2643–2649 - PubMed
-
- Chang B. D., Broude E. V., Dokmanovic M., Zhu H., Ruth A., Xuan Y., Kandel E. S., Lausch E., Christov K., Roninson I. B. (1999) A senescence-like phenotype distinguishes tumor cells that undergo terminal proliferation arrest after exposure to anticancer agents. Cancer Res. 59, 3761–3767 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

