Nucleus accumbens GLP-1 receptors influence meal size and palatability
- PMID: 23612998
- PMCID: PMC3680699
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00137.2013
Nucleus accumbens GLP-1 receptors influence meal size and palatability
Abstract
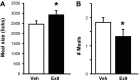
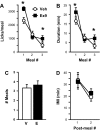
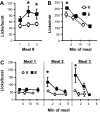
Recent evidence suggests that the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) neuronal projection to the nucleus accumbens core (NAcC) contributes to food intake control. To investigate the role of endogenous stimulation of GLP-1 receptors (GLP-1R) in NAcC, we examined the effects of the GLP-1R antagonist exendin-(9-39) (Ex9) on meal pattern and microstructure of ingestive behavior in rats. Intra-NAcC Ex9 treatment selectively increased meal size relative to vehicle in rats consuming 0.25 M sucrose solution or sweetened condensed milk. Microstructural analysis revealed effects of NAcC Ex9 on initial lick rate and the size and duration of licking bursts in rats consuming 0.1 or 0.25 M sucrose, suggesting that blockade of NAcC GLP-1R increases palatability. Because NAcC Ex9 did not affect licking for nonnutritive saccharin (0.1%), we suggest that the presence of nutrients in the gut may be required for endogenous stimulation of NAcC GLP-1R. Consistent with this, we also found that the meal size-suppressive effects of intragastric nutrient infusion were attenuated by NAcC delivery of Ex9 at a dose that had no effect when delivered alone. Analysis of licking patterns revealed that NAcC Ex9 did not reverse intragastric nutrient-induced suppression of burst number but rather blunted the effect of nutrient infusion on meal size primarily by increasing the size and duration of licking bursts. Together, our results suggest that NAcC Ex9 influences taste evaluation. We conclude that GLP-1 released in NAcC in response to gastrointestinal nutrients reduces the hedonic value of food.
Keywords: glucagon-like peptide-1; licking microstructure; nucleus accumbens; palatability; satiation.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors in nucleus accumbens affect food intake.J Neurosci. 2011 Oct 12;31(41):14453-7. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3262-11.2011. J Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21994361 Free PMC article.
-
mu-Opioid receptor stimulation in the nucleus accumbens elevates fatty tastant intake by increasing palatability and suppressing satiety signals.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011 Jul;301(1):R244-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00406.2010. Epub 2011 May 4. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2011. PMID: 21543633 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous hindbrain glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor activation contributes to the control of food intake by mediating gastric satiation signaling.Endocrinology. 2009 Jun;150(6):2654-9. doi: 10.1210/en.2008-1479. Epub 2009 Mar 5. Endocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19264875 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and satiation.Physiol Behav. 2011 Nov 30;105(1):71-6. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.02.038. Epub 2011 Mar 1. Physiol Behav. 2011. PMID: 21371486 Review.
-
Neural integration of satiation and food reward: role of GLP-1 and orexin pathways.Physiol Behav. 2014 Sep;136:194-9. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.03.013. Epub 2014 Mar 18. Physiol Behav. 2014. PMID: 24650552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Peripheral interleukin-2 level is associated with negative symptoms and cognitive performance in schizophrenia.Physiol Behav. 2014 Apr 22;129:194-8. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.02.032. Epub 2014 Feb 25. Physiol Behav. 2014. PMID: 24576679
-
Semaglutide lowers body weight in rodents via distributed neural pathways.JCI Insight. 2020 Mar 26;5(6):e133429. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.133429. JCI Insight. 2020. PMID: 32213703 Free PMC article.
-
The Phantom Satiation Hypothesis of Bariatric Surgery.Front Neurosci. 2021 Feb 1;15:626085. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.626085. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 33597843 Free PMC article.
-
Liraglutide and obesity: a review of the data so far.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Mar 30;9:1867-75. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S58459. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 25848222 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The diverse effects of brain glucagon-like peptide 1 receptors on ingestive behaviour.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Feb;179(4):571-583. doi: 10.1111/bph.15535. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33990944 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baird JP, Grill HJ, Kaplan JM. Effect of hepatic glucose infusion on glucose intake and licking microstructure in deprived and nondeprived rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 277: R1136–R1143, 1999 - PubMed
-
- Berridge KC. Measuring hedonic impact in animals and infants: microstructure of affective taste reactivity patterns. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 24: 173–198, 2000 - PubMed
-
- Breslin PA, Davis JD, Rosenak R. Saccharin increases the effectiveness of glucose in stimulating ingestion in rats but has little effect on negative feedback. Physiol Behav 60: 411–416, 1996 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

