Searching for unpublished data for Cochrane reviews: cross sectional study
- PMID: 23613540
- PMCID: PMC3633324
- DOI: 10.1136/bmj.f2231
Searching for unpublished data for Cochrane reviews: cross sectional study
Abstract
Objective: To describe the experiences of authors of Cochrane reviews in searching for, getting access to, and using unpublished data.
Design: Cross sectional study.
Setting: Cochrane reviews.
Participants: 2184 corresponding authors of Cochrane reviews as of May 2012.
Main outcome measure: Frequencies of responses to open ended and closed questions in an online survey.
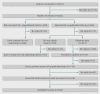
Results: Of 5915 authors contacted by email, 2184 replied (36.9% response rate). Of those, 1656 (75.8%) had searched for unpublished data. In 913 cases (55.1% of 1656), new data were obtained and we received details about these data for 794 data sources. The most common data source was "trialists/investigators," accounting for 73.9% (n=587) of the 794 data sources. Most of the data were used in the review (82.0%, 651/794) and in 53.4% (424/794) of cases data were provided in less than a month. Summary data were most common, provided by 50.8% (403/794) of the data sources, whereas 20.5% (163/794) provided individual patient data. In only 6.3% (50/794) of cases were data reported to have been obtained from the manufacturers, and this group waited longer and had to make more contacts to get the data. The data from manufacturers were less likely to be for individual patients and less likely to be used in the review. Data from regulatory agencies accounted for 3.0% (24/794) of the obtained data.
Conclusions: Most authors of Cochrane reviews who searched for unpublished data received useful information, primarily from trialists. Our response rate was low and the authors who did not respond were probably less likely to have searched for unpublished data. Manufacturers and regulatory agencies were uncommon sources of unpublished data.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
References
-
- Scherer RW, Langenberg P, von Elm E. Full publication of results initially presented in abstracts. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;(2):MR000005. - PubMed
-
- Turner EH, Matthews AM, Linardatos E, Tell RA, Rosenthal R. Selective publication of antidepressant trials and its influence on apparent efficacy. N Engl J Med 2008;358:252-60. - PubMed
-
- Chan AW, Hrobjartsson A, Haahr MT, Gotzsche PC, Altman DG. Empirical evidence for selective reporting of outcomes in randomized trials: comparison of protocols to published articles. JAMA 2004;291:2457-65. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources