Glucose variability: where it is important and how to measure it
- PMID: 23613566
- PMCID: PMC3636643
- DOI: 10.2337/db12-1610
Glucose variability: where it is important and how to measure it
Abstract
Glucose variability predicts hypoglycemia in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes and has consistently been related to mortality in nondiabetic patients in the intensive care unit. SD and mean amplitude of glycemic excursions have historically been very popular measures of glucose variability. For reasons outlined in this counterpoint, I propose to use coefficient of variation and the mean absolute glucose change as preferred measures of glucose variability.
Figures
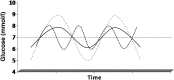

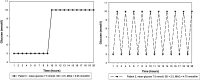
References
-
- Siegelaar SE, Holleman F, Hoekstra JB, DeVries JH. Glucose variability; does it matter? Endocr Rev 2010;31:171–182 - PubMed
-
- Rodbard D. Clinical interpretation of indices of quality of glycemic control and glycemic variability. Postgrad Med 2011;123:107–118 - PubMed
-
- Cox DJ, Kovatchev BP, Julian DM, et al. Frequency of severe hypoglycemia in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus can be predicted from self-monitoring blood glucose data. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1994;79:1659–1662 - PubMed
-
- Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Goode K, Atkin SL. Relating mean blood glucose and glucose variability to the risk of multiple episodes of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007;50:2553–2561 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

