Differential targeting of brain stress circuits with a selective glucocorticoid receptor modulator
- PMID: 23613579
- PMCID: PMC3651427
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1219411110
Differential targeting of brain stress circuits with a selective glucocorticoid receptor modulator
Abstract
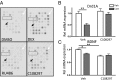
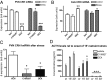
Glucocorticoid receptor (GR) antagonism may be of considerable therapeutic value in stress-related psychopathology such as depression. However, blockade of all GR-dependent processes in the brain will lead to unnecessary and even counteractive effects, such as elevated endogenous cortisol levels. Selective GR modulators are ligands that can act both as agonist and as antagonist and may be used to separate beneficial from harmful treatment effects. We have discovered that the high-affinity GR ligand C108297 is a selective modulator in the rat brain. We first demonstrate that C108297 induces a unique interaction profile between GR and its downstream effector molecules, the nuclear receptor coregulators, compared with the full agonist dexamethasone and the antagonist RU486 (mifepristone). C108297 displays partial agonistic activity for the suppression of hypothalamic corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH) gene expression and potently enhances GR-dependent memory consolidation of training on an inhibitory avoidance task. In contrast, it lacks agonistic effects on the expression of CRH in the central amygdala and antagonizes GR-mediated reduction in hippocampal neurogenesis after chronic corticosterone exposure. Importantly, the compound does not lead to disinhibition of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis. Thus, C108297 represents a class of ligands that has the potential to more selectively abrogate pathogenic GR-dependent processes in the brain, while retaining beneficial aspects of GR signaling.
Keywords: HPA axis; NCoA1; neuroendocrinology; steroid pharmacology; transcription regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: J.K.B. and H.H. are employees of Corcept Therapeutics, which develops glucocorticoid receptor ligands for clinical use. Corcept Therapeutics has provided compounds and financed part of the experiments. R.H. is an employee of Pamgene International, which provided the peptide arrays used in this study.
Figures
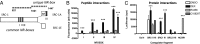

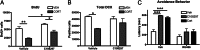
References
-
- de Kloet ER, Joëls M, Holsboer F. Stress and the brain: From adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2005;6(6):463–475. - PubMed
-
- Nieman LK, et al. Successful treatment of Cushing’s syndrome with the glucocorticoid antagonist RU 486. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1985;61(3):536–540. - PubMed
-
- DeBattista C, et al. Mifepristone versus placebo in the treatment of psychosis in patients with psychotic major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2006;60(12):1343–1349. - PubMed
-
- Rosenfeld P, Van Eekelen JA, Levine S, De Kloet ER. Ontogeny of the type 2 glucocorticoid receptor in discrete rat brain regions: An immunocytochemical study. Brain Res. 1988;470(1):119–127. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

