Prognostic significance of EBV latent membrane protein 1 expression in lymphomas: evidence from 15 studies
- PMID: 23613723
- PMCID: PMC3629080
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0060313
Prognostic significance of EBV latent membrane protein 1 expression in lymphomas: evidence from 15 studies
Abstract
Background: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection has been associated with lymphoma development. EBV latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) is essential for EBV-mediated transformation and progression of different human cells, including lymphocytes. This meta-analysis investigated LMP1 expression with prognosis of patients with lymphoma.
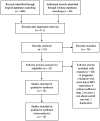
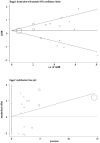
Methods: The electronic databases of PubMed, Embase, and Chinese Biomedicine Databases were searched. There were 15 published studies available for a random effects model analysis. Quality assessment was performed using the Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale for cohort studies. A funnel plot was used to investigate publication bias, and sources of heterogeneity were identified by meta-regression analysis. The combined hazard ratios (HR) and their corresponding 95% confidence intervals of LMP1 expression were calculated by comparison to the overall survival.
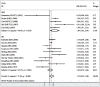
Results: Overall, there was no statistical significance found between LMP1 expression and survival of lymphoma patients (HR 1.25 [95% CI, 0.92-1.68]). In subgroup analyses, LMP1 expression was associated with survival in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) (HR = 1.84, 95% CI: 1.02-3.34), but not with survival of patients with Hodgkin disease (HD) (HR = 1.03, 95% CI: 0.74-1.44). In addition, significant heterogeneity was present and the meta-regression revealed that the outcome of analysis was mainly influenced by the cutoff value.
Conclusions: This meta-analysis demonstrated that LMP1 expression appears to be an unfavorable prognostic factor for overall survival of NHL patients. The data suggested that EBV infection and LMP1 expression may be an important factor for NHL development or progression.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of latent membrane protein 1 expression on overall survival in Epstein-Barr virus-associated cancers: a literature-based meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):29311-23. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4906. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26336130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of latent membrane protein 1 expression in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(14):e6512. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006512. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28383415 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of frequency of epstein-barr virus in non- Hodgkin lymphomas Using EBV latent membrane protein 1 (EBV-LMP1) immunohistochemical staining.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(6):3963-7. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.6.3963. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23886215
-
Epstein-Barr virus encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) and TNF receptor associated factors (TRAF): colocalisation of LMP1 and TRAF1 in primary EBV infection and in EBV associated Hodgkin lymphoma.Mol Pathol. 2003 Jun;56(3):156-61. doi: 10.1136/mp.56.3.156. Mol Pathol. 2003. PMID: 12782762 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of Epstein-Barr virus DNA in NK/T-cell lymphoma: a meta-analysis.Onco Targets Ther. 2018 Feb 26;11:997-1004. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S153942. eCollection 2018. Onco Targets Ther. 2018. PMID: 29520150 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A neutralized human LMP1-IgG inhibits ENKTL growth by suppressing the JAK3/STAT3 signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Feb 14;8(7):10954-10965. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14032. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28009988 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of latent membrane protein 1 expression on overall survival in Epstein-Barr virus-associated cancers: a literature-based meta-analysis.Oncotarget. 2015 Oct 6;6(30):29311-23. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4906. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26336130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic significance of latent membrane protein 1 expression in non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Apr;96(14):e6512. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006512. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017. PMID: 28383415 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Epstein-Barr Virus LMP-1 Immunohistochemical Staining in Childhood Hodgkin Lymphoma.Iran J Pediatr. 2015 Dec;25(6):e2359. doi: 10.5812/ijp.2359. Epub 2015 Dec 23. Iran J Pediatr. 2015. PMID: 26635935 Free PMC article.
-
Pathologically Relevant Mouse Models for Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated B Cell Lymphoma.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 24;12:639844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.639844. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33732260 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Takahashi E, Ohshima K, Kimura H, Hara K, Suzuki R, et al. (2011) Clinicopathological analysis of the age-related differences in patients with Epstein–Barr virus (EBV)-associated extranasal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma with reference to the relationship with aggressive NK cell leukaemia and chronic active EBV infection-associated lymphoproliferative disorders. Histopathology 59: 660–71. - PubMed
-
- Carbone A, Gloghini A, Dotti G (2008) EBV-associated lymphoproliferative disorders: classification and treatment. Oncologist 13: 577–85. - PubMed
-
- Morris MA, Dawson CW, Young LS (2009) Role of the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein-1, LMP1, in the pathogenesis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Future Oncol 5: 811–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

