Reproductive capability is associated with lifespan and cause of death in companion dogs
- PMID: 23613790
- PMCID: PMC3629191
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061082
Reproductive capability is associated with lifespan and cause of death in companion dogs
Abstract
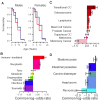
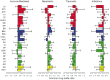
Reproduction is a risky affair; a lifespan cost of maintaining reproductive capability, and of reproduction itself, has been demonstrated in a wide range of animal species. However, little is understood about the mechanisms underlying this relationship. Most cost-of-reproduction studies simply ask how reproduction influences age at death, but are blind to the subjects' actual causes of death. Lifespan is a composite variable of myriad causes of death and it has not been clear whether the consequences of reproduction or of reproductive capability influence all causes of death equally. To address this gap in understanding, we compared causes of death among over 40,000 sterilized and reproductively intact domestic dogs, Canis lupus familiaris. We found that sterilization was strongly associated with an increase in lifespan, and while it decreased risk of death from some causes, such as infectious disease, it actually increased risk of death from others, such as cancer. These findings suggest that to understand how reproduction affects lifespan, a shift in research focus is needed. Beyond the impact of reproduction on when individuals die, we must investigate its impact on why individuals die, and subsequently must identify the mechanisms by which these causes of death are influenced by the physiology associated with reproductive capability. Such an approach may also clarify the effects of reproduction on lifespan in people.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Flatt T (2011) Survival costs of reproduction in Drosophila . Experimental gerontology 46: 369–375. - PubMed
-
- Partridge L, Gems D, Withers DJ (2005) Sex and death: what is the connection? Cell 120: 461–472. - PubMed
-
- Chapman T, Liddle LF, Kalb JM, Wolfner MF, Partridge L (1995) Cost of mating in Drosophila melanogaster is mediated by male accessory gland products. Nature 373: 241–244. - PubMed
-
- Partridge L, Harvey P (1985) Costs of reproduction. Nature 316: 20.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

