Superoxide mediates direct current electric field-induced directional migration of glioma cells through the activation of AKT and ERK
- PMID: 23613809
- PMCID: PMC3629049
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061195
Superoxide mediates direct current electric field-induced directional migration of glioma cells through the activation of AKT and ERK
Abstract
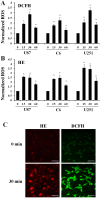
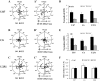
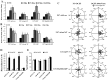
Direct current electric fields (DCEFs) can induce directional migration for many cell types through activation of intracellular signaling pathways. However, the mechanisms that bridge extracellular electrical stimulation with intracellular signaling remain largely unknown. In the current study, we found that a DCEF can induce the directional migration of U87, C6 and U251 glioma cells to the cathode and stimulate the production of hydrogen peroxide and superoxide. Subsequent studies demonstrated that the electrotaxis of glioma cells were abolished by the superoxide inhibitor N-acetyl-l-cysteine (NAC) or overexpression of mitochondrial superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), but was not affected by inhibition of hydrogen peroxide through the overexpression of catalase. Furthermore, we found that the presence of NAC, as well as the overexpression of MnSOD, could almost completely abolish the activation of Akt, extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (Erk)1/2, c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and p38, although only JNK and p38 were affected by overexpression of catalase. The presenting of specific inhibitors can decrease the activation of Erk1/2 or Akt as well as the directional migration of glioma cells. Collectively, our data demonstrate that superoxide may play a critical role in DCEF-induced directional migration of glioma cells through the regulation of Akt and Erk1/2 activation. This study provides novel evidence that the superoxide is at least one of the "bridges" coupling the extracellular electric stimulation to the intracellular signals during DCEF-mediated cell directional migration.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Sato M, Ueda M, Takagi H, Watanabe T, Yanagida T (2007) Input–output relationship in galvanotactic response of Dictyostelium cells. Biosystems 88: 261–272. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Nandagopal S, Wu D, Romanuik SF, Paul K, et al. (2011) Activated T lymphocytes migrate toward the cathode of DC electric fields in microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 11: 1298–1304. - PubMed
-
- Zhao M (2009) Electrical fields in wound healing-An overriding signal that directs cell migration. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 20: 674–682. - PubMed
-
- Yan X, Han J, Zhang Z, Wang J, Cheng Q, et al. (2009) Lung cancer A549 cells migrate directionally in DC electric fields with polarized and activated EGFRs. Bioelectromagnetics 30: 29–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

