Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) protein expression and activity after dopaminergic and noradrenergic lesions of the rat brain
- PMID: 23613844
- PMCID: PMC3628796
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061392
Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) protein expression and activity after dopaminergic and noradrenergic lesions of the rat brain
Abstract
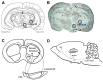
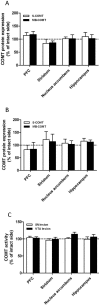
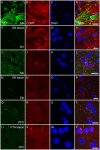
The occurrence of catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) in presynaptic neurons remains controversial. This study utilized dopaminergic and noradrenergic toxins to assess the presence of COMT in the presynaptic neurons originating from the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area or locus coeruleus. Destruction of dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons was assessed by measuring the dopamine and noradrenaline content in the projection areas of these neurons. Additionally, COMT protein expression and activity were examined in several projection areas to determine whether there are any changes in COMT values. Colocalization studies were done to identify COMT-containing postsynaptic neurons. Despite successful lesioning of dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons, no changes in COMT protein expression or activity could be noted. These results strongly suggest that COMT is not present in presynaptic dopaminergic and noradrenergic neurons. There was a high colocalization of COMT with the GABAergic marker of short neurons both in the striatum and cortex but only a weak, if any, with the cholinergic marker in the cortex.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Männistö PT, Kaakkola S (1999) Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT): Biochemistry, molecular biology, pharmacology, and clinical efficacy of the new selective COMT inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev 51: 593–628. - PubMed
-
- Kaakkola S, Männistö PT, Nissinen E (1987) Striatal membrane-bound and soluble catechol-O-methyl-transferase after selective neuronal lesions in the rat. J Neur Transm 69: 221–228. - PubMed
-
- Kaplan GP, Hartman BK, Creveling CR (1981) Localization of catechol-O-methyltransferase in the leptomeninges, choroid plexus and ciliary epithelium: Implications for the separation of central and peripheral catechols. Brain Res 204: 353–360. - PubMed
-
- Rivett AJ, Francis A, Roth JA (1983) Distinct cellular localization of membrane-bound and soluble forms of catechol-O-methyltransferase in brain. J Neurochem 40: 215–219. - PubMed
-
- Karhunen T, Tilgmann C, Ulmanen I, Panula P (1995) Catechol-O-methyltransferase (COMT) in rat brain: Immunoelectron microscopic study with an antiserum against rat recombinant COMT protein. Neurosc Lett 187: 57–60. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

