The novel pro-osteogenic activity of NUCB2(1-83.)
- PMID: 23613885
- PMCID: PMC3626684
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061619
The novel pro-osteogenic activity of NUCB2(1-83.)
Abstract
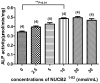
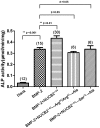
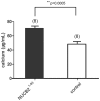
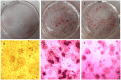
NUCB2¹⁻⁸³ has been recently reported as an anorexigenic and anti-hyperglycemic peptide. Here we report that NUCB2¹⁻⁸³ promotes osteogenesis. It was found after two months of once-a-day intravenous injection of NUCB2¹⁻⁸³, bone mineral density of femora and lumbar vertebrae were increased in ovariectomized rats. NUCB2¹⁻⁸³ also increased the alkaline phosphatase activity and promoted mineralization in mouse MC3T3-E1 preosteoblastic cell line. When either both Arg⁶⁰ and Arg⁶³ or Ser⁷² were mutated to Ala, the pro-osteogenic activity was completely lost, indicating that these residues are structurally important for its biological function. Furthermore, it encumbered osteoclastic differentiation of RAW 264.7 macrophage. It also excluded any possibility of the effect caused by contaminants or experimental faults, and demonstrated that the pro-osteogenic activity observed was a specific effect of NUCB2¹⁻⁸³ itself. These findings warranted that further studies on NUCB2¹⁻⁸³ would be valuable for the treatment of bone metabolic diseases especially for osteoporosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Cummings SR, Melton LJ (2002) Epidemiology and outcomes of osteoporotic fractures. Lancet 359: 1761–1767. - PubMed
-
- Melton LJ III, Cooper C (2001) Magnitude and impact of osteoporosis and fractures, In: Marcus R, Feldman D, Kelsey J, eds. Osteoporosis. 2nd edn (vol 1), San Diego. Academic Press: 557–567.
-
- Melton LJ III, Johnell O, Lau E, Mautalen CA, Seeman E (2004) Osteoporosis and the global competition for health care resources. J Bone Miner Res 19: 1055–1058. - PubMed
-
- Sambrook P, Cooper C (2006) Osteoporosis. Lancet 367: 2010–2018. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

