De-regulated microRNAs in pediatric cancer stem cells target pathways involved in cell proliferation, cell cycle and development
- PMID: 23613887
- PMCID: PMC3629228
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061622
De-regulated microRNAs in pediatric cancer stem cells target pathways involved in cell proliferation, cell cycle and development
Abstract
Background: microRNAs (miRNAs) have been implicated in the control of many biological processes and their deregulation has been associated with many cancers. In recent years, the cancer stem cell (CSC) concept has been applied to many cancers including pediatric. We hypothesized that a common signature of deregulated miRNAs in the CSCs fraction may explain the disrupted signaling pathways in CSCs.
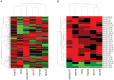
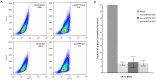
Methodology/results: Using a high throughput qPCR approach we identified 26 CSC associated differentially expressed miRNAs (DEmiRs). Using BCmicrO algorithm 865 potential CSC associated DEmiR targets were obtained. These potential targets were subjected to KEGG, Biocarta and Gene Ontology pathway and biological processes analysis. Four annotated pathways were enriched: cell cycle, cell proliferation, p53 and TGF-beta/BMP. Knocking down hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-181c-5p and hsa-miR-135b-5p using antisense oligonucleotides and small interfering RNA in cell lines led to the depletion of the CSC fraction and impairment of sphere formation (CSC surrogate assays).
Conclusion: Our findings indicated that CSC associated DEmiRs and the putative pathways they regulate may have potential therapeutic applications in pediatric cancers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of colorectal cancer stem cell survival and invasive potential by hsa-miR-140-5p mediated suppression of Smad2 and autophagy.Oncotarget. 2015 Aug 14;6(23):19735-46. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3771. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 25980495 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA profiling reveals dysregulated microRNAs and their target gene regulatory networks in cemento-ossifying fibroma.J Oral Pathol Med. 2018 Jan;47(1):78-85. doi: 10.1111/jop.12650. Epub 2017 Nov 1. J Oral Pathol Med. 2018. PMID: 29032608
-
MiRNAs Mediate GDNF-Induced Proliferation and Migration of Glioma Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):1923-1938. doi: 10.1159/000485883. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29224008
-
Modulatory roles of microRNAs in the regulation of different signalling pathways in large bowel cancer stem cells.Biol Cell. 2016 Mar;108(3):51-64. doi: 10.1111/boc.201500062. Epub 2016 Feb 2. Biol Cell. 2016. PMID: 26712035 Review.
-
MicroRNAs involved in regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells as molecular targets for cancer therapeutics.Cancer Gene Ther. 2012 Nov;19(11):723-30. doi: 10.1038/cgt.2012.58. Epub 2012 Sep 14. Cancer Gene Ther. 2012. PMID: 22975591 Review.
Cited by
-
microRNA 490-3P enhances the drug-resistance of human ovarian cancer cells.J Ovarian Res. 2014 Aug 31;7:84. doi: 10.1186/s13048-014-0084-4. J Ovarian Res. 2014. PMID: 25297343 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Ovarian Epithelial Carcinoma Tumorigenesis and Progression by microRNA 106b Mediated through the RhoC Pathway.PLoS One. 2015 May 1;10(5):e0125714. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0125714. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 25933027 Free PMC article.
-
Nanoparticles for Drug and Gene Delivery in Pediatric Brain Tumors' Cancer Stem Cells: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 2;15(2):505. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020505. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36839827 Free PMC article. Review.
-
RhoC is a major target of microRNA-93-5P in epithelial ovarian carcinoma tumorigenesis and progression.Mol Cancer. 2015 Feb 4;14(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0304-6. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25649143 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA expression patterns and signalling pathways in the development and progression of childhood solid tumours.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jan 19;16(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0584-0. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28103887 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hatfield SD, Shcherbata HR, Fischer KA, Nakahara K, Carthew RW, et al. (2005) Stem cell division is regulated by the microRNA pathway. Nature 435: 974–978. - PubMed
-
- Zhang B, Pan X, Anderson TA (2006) MicroRNA: a new player in stem cells. Journal of cellular physiology 209: 266–269. - PubMed
-
- Yu F, Yao H, Zhu P, Zhang X, Pan Q, et al. (2007) let-7 regulates self renewal and tumorigenicity of breast cancer cells. Cell 131: 1109–1123. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

