PKG II inhibits EGF/EGFR-induced migration of gastric cancer cells
- PMID: 23613900
- PMCID: PMC3627897
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061674
PKG II inhibits EGF/EGFR-induced migration of gastric cancer cells
Abstract
Background: Our previous research results showed that Type II cGMP dependent protein kinase (PKG II) could block the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and consequently inhibit the proliferation and the related MAPK/ERK-mediated signal transduction of gastric cancer cell line BGC-823, suggesting that PKG II might inhibit other EGFR-triggered signal transduction pathways and related biological activities of gastric cancer cells. This paper was designed to investigate the potential inhibition of PKG II on EGF/EGFR-induced migration activity and the related signal transduction pathways.
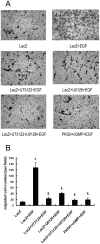
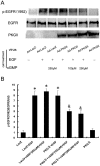
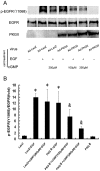
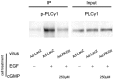
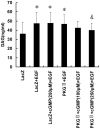
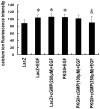
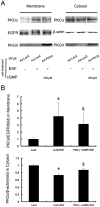
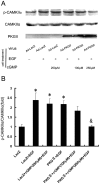
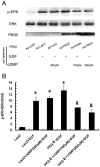
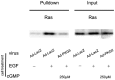
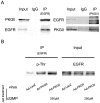
Methodology/principal findings: In gastric cancer cell line AGS, expression and activity of PKG II were increased by infecting the cells with adenoviral construct encoding PKG II cDNA (Ad-PKG II) and treating the cells with cGMP analogue 8-pCPT-cGMP. Phosphorylation of proteins was detected by Western Blotting and active small G protein Ras and Rac1 was measured by "Pull-down" method. Cell migration activity was detected with trans-well equipment. Binding between PKG II and EGFR was detected with Co-IP. The results showed EGF stimulated migration of AGS cell and the effect was related to PLCγ1 and ERK-mediated signal transduction pathways. PKG II inhibited EGF-induced migration activity and blocked EGF-initiated signal transduction of PLCγ1 and MAPK/ERK-mediated pathways through preventing EGF-induced Tyr 992 and Tyr 1068 phosphorylation of EGFR. PKG II bound with EGFR and caused threonine phosphorylation of it.
Conclusion/significance: Our results systemically confirms the inhibition of PKG II on EGF-induced migration and related signal transduction of PLCγ1 and MAPK/ERK-mediated pathways, indicating that PKG II has a fargoing inhibition on EGF/EGFR related signal transduction and biological activities of gastric cancer cells through phosphorylating EGFR and blocking the activation of it.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
PKG II effectively reversed EGF-induced protein expression alterations in human gastric cancer cell lines.Cell Biol Int. 2018 Apr;42(4):435-442. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10912. Epub 2017 Dec 14. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 29150923
-
Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits ligand‑induced activation of EGFR in gastric cancer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2014 Apr;9(4):1405-9. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.1942. Epub 2014 Feb 10. Mol Med Rep. 2014. PMID: 24534906
-
Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits EGF-triggered signal transduction of the MAPK/ERK-mediated pathway in gastric cancer cells.Oncol Rep. 2012 Feb;27(2):553-8. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1507. Epub 2011 Oct 13. Oncol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22012247
-
Role of EGF Receptor Regulatory Networks in the Host Response to Viral Infections.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022 Jan 10;11:820355. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.820355. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35083168 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When ubiquitination meets phosphorylation: a systems biology perspective of EGFR/MAPK signalling.Cell Commun Signal. 2013 Jul 31;11:52. doi: 10.1186/1478-811X-11-52. Cell Commun Signal. 2013. PMID: 23902637 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
LncRNA EMX2OS, Regulated by TCF12, Interacts with FUS to Regulate the Proliferation, Migration and Invasion of Prostate Cancer Cells Through the cGMP-PKG Signaling Pathway.Onco Targets Ther. 2020 Jul 21;13:7045-7056. doi: 10.2147/OTT.S243552. eCollection 2020. Onco Targets Ther. 2020. PMID: 32801740 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphodiesterase 10A is overexpressed in lung tumor cells and inhibitors selectively suppress growth by blocking β-catenin and MAPK signaling.Oncotarget. 2017 Aug 27;8(41):69264-69280. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.20566. eCollection 2017 Sep 19. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 29050202 Free PMC article.
-
Matrine suppresses invasion and metastasis of NCI-H1299 cells by enhancing microRNA-133a expression.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015 Jul 15;8(7):10714-22. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015. PMID: 26379863 Free PMC article.
-
Rotundarpene inhibits TNF-α-induced activation of the Akt, mTOR, and NF-κB pathways, and the JNK and p38 associated with production of reactive oxygen species.Mol Cell Biochem. 2017 Oct;434(1-2):113-125. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3041-x. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28432555
-
Type II cyclic guanosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor activation in different cancer cell lines.Oncol Lett. 2015 Jun;9(6):2781-2786. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3067. Epub 2015 Mar 23. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 26137146 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cook AL, Haynes JM (2004) Protein kinase G II-mediated proliferative effects in human cultured prostatic stromal cells. Cell Signal 16: 253–261. - PubMed
-
- Fallahian F, Karami-Tehrani F, Salami S (2011) Cyclic GMP induced apoptosis via protein kinase G in oestrogen receptor-positive and -negative breast cancer cell lines. FEBS Journal 278: 3360–3369. - PubMed
-
- Yang SQ, Chen YC, Wang Y, Tao Y (2008) Expression of cGMP dependent protein kinase II in cancer cell lines was obviously decreased. J Jiangsu Univ (Medicine edition) 1: 5–7.
-
- Chen YC, Ren F, Sang JR, Tao Y, Xu WR (2010) Type II cGMP-dependent protein kinase inhibits proliferation of the gastric cancer cell line BGC-823. Molecular Medicine Reports 3: 361–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

