Is serum zinc level associated with prediabetes and diabetes?: a cross-sectional study from Bangladesh
- PMID: 23613929
- PMCID: PMC3629219
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061776
Is serum zinc level associated with prediabetes and diabetes?: a cross-sectional study from Bangladesh
Abstract
Aims: To determine serum zinc level and other relevant biological markers in normal, prediabetic and diabetic individuals and their association with Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA) parameters.
Methods: This cross-sectional study was conducted between March and December 2009. Any patient aged ≥ 30 years attending the medicine outpatient department of a medical university hospital in Dhaka, Bangladesh and who had a blood glucose level ordered by a physician was eligible to participate.
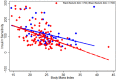
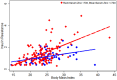
Results: A total of 280 participants were analysed. On fasting blood sugar results, 51% were normal, 13% had prediabetes and 36% had diabetes. Mean serum zinc level was lowest in prediabetic compared to normal and diabetic participants (mean differences were approximately 65 ppb/L and 33 ppb/L, respectively). In multiple linear regression, serum zinc level was found to be significantly lower in prediabetes than in those with normoglycemia. Beta cell function was significantly lower in prediabetes than normal participants. Adjusted linear regression for HOMA parameters did not show a statistically significant association between serum zinc level, beta cell function (P = 0.07) and insulin resistance (P = 0.08). Low serum zinc accentuated the increase in insulin resistance seen with increasing BMI.
Conclusion: Participants with prediabetes have lower zinc levels than controls and zinc is significantly associated with beta cell function and insulin resistance. Further longitudinal population based studies are warranted and controlled trials would be valuable for establishing whether zinc supplementation in prediabetes could be a useful strategy in preventing progression to Type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Is serum zinc associated with pancreatic beta cell function and insulin sensitivity in pre-diabetic and normal individuals? Findings from the Hunter Community Study.PLoS One. 2014 Jan 8;9(1):e83944. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083944. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24416185 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship of Soluble RAGE with Insulin Resistance and Beta Cell Function during Development of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.J Diabetes Res. 2015;2015:150325. doi: 10.1155/2015/150325. Epub 2015 May 19. J Diabetes Res. 2015. PMID: 26078977 Free PMC article.
-
Serum ferritin and glucose homeostasis: change in the association by glycaemic state.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015 Jul;31(5):507-14. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2628. Epub 2015 Feb 3. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2015. PMID: 25470760
-
Associations of vitamin D with insulin resistance, obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018 Jan;175:177-189. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.09.017. Epub 2016 Sep 20. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 27662816 Review.
-
Inulin-type fructans supplementation improves glycemic control for the prediabetes and type 2 diabetes populations: results from a GRADE-assessed systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of 33 randomized controlled trials.J Transl Med. 2019 Dec 5;17(1):410. doi: 10.1186/s12967-019-02159-0. J Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31805963 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Effect of glycation on human serum albumin-zinc interaction: a biophysical study.J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018 May;23(3):447-458. doi: 10.1007/s00775-018-1554-8. Epub 2018 Apr 4. J Biol Inorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29619544
-
Zinc supplementation for the prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus in adults with insulin resistance.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 May 28;2015(5):CD005525. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005525.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. PMID: 26020622 Free PMC article.
-
Nutritional Support for Bariatric Surgery Patients: The Skin beyond the Fat.Nutrients. 2021 May 6;13(5):1565. doi: 10.3390/nu13051565. Nutrients. 2021. PMID: 34066564 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The associations between serum zinc levels and metabolic syndrome in the Korean population: findings from the 2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.PLoS One. 2014 Aug 25;9(8):e105990. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0105990. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25153887 Free PMC article.
-
Zinc Ameliorates the Osteogenic Effects of High Glucose in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells.Cells. 2021 Nov 9;10(11):3083. doi: 10.3390/cells10113083. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34831306 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Berry C, Tardif J-C, Bourassa MG (2007) Coronary Heart Disease in Patients With Diabetes. J Am Coll Cardiol 49: 631–642. - PubMed
-
- Wild S, Roglic G, Green A, Sicree R, King H (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27: 1047–1053. - PubMed
-
- Rathmann W, Giani G (2004) Global prevalence of diabetes: estimates for the year 2000 and projections for 2030. Diabetes Care 27: 2568–2569 author reply 2569. - PubMed
-
- Benjamin SM, Valdez R, Geiss LS, Rolka DB, Venkat Narayan KM (2003) Estimated Number of Adults With Prediabetes in the U.S. in 2000: Opportunities for prevention. Diabetes Care 26: 645–649. - PubMed
-
- Reaven GM (1988) Role of Insulin Resistance in Human Disease. Diabetes 37: 1595–1607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

