Chicken cathelicidins display antimicrobial activity against multiresistant bacteria without inducing strong resistance
- PMID: 23613986
- PMCID: PMC3632573
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0061964
Chicken cathelicidins display antimicrobial activity against multiresistant bacteria without inducing strong resistance
Abstract
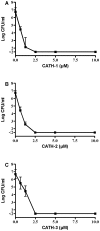
The increased prevalence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria in combination with the relatively limited development of new antibiotics presents a serious threat to public health. In chicken, especially Extended-Spectrum ß-Lactamase (ESBL) carrying Enterobacteriaceae are often asymptomatically present but can infect humans. Due to their broad range antimicrobial activity cathelicidins and other host defence peptides, are considered to be an attractive alternative to conventional antibiotics. In this study, the antimicrobial activity of three chicken cathelicidins against a broad array of multidrug resistant bacteria was determined. All three peptides showed high antibacterial activity independent of the presence of MDR characteristics. Induction experiments using S. aureus and K. pneumoniae showed that although an increase in resistance was initially observed, susceptibility towards chicken cathelicidins remained high and no major resistance was developed. The combined results underline the potential of chicken cathelicidins as a new alternative to antibiotics.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Woodford N, Turton JF, Livermore DM (2011) Multiresistant Gram-negative bacteria: The role of high-risk clones in the dissemination of antibiotic resistance. FEMS Microbiol Rev 35: 736–755. - PubMed
-
- Gould IM, David MZ, Esposito S, Garau J, Lina G, et al. (2012) New insights into meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) pathogenesis, treatment and resistance. Int J of Antimicrob Agents 39: 96–104. - PubMed
-
- Fluit AC (2012) Livestock-associated Staphylococcus aureus . Clin Microbiol Infect 18: 735–744. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

