Total plasma protein in very preterm babies: prognostic value and comparison with illness severity scores
- PMID: 23614036
- PMCID: PMC3628347
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0062210
Total plasma protein in very preterm babies: prognostic value and comparison with illness severity scores
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to investigate the predictive value for severe adverse outcome of plasma protein measurements on day one of life in very preterm infants and to compare total plasma protein levels with the validated illness severity scores CRIB, CRIB-II, SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II, regarding their predictive ability for severe adverse outcome.
Methods: We analyzed a cohort of infants born at 24-31 weeks gestation, admitted to the tertiary intensive care unit of a university hospital over 10.5 years. The outcome measure was "severe adverse outcome" defined as death before discharge or severe neurological injury on cranial ultrasound. The adjusted odd ratio (aOR) and 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of severe adverse outcome for hypoproteinemia (total plasma protein level <40 g/L) was calculated by univariate and multivariate analyses. Calibration (Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit) was performed and the predictive ability for severe adverse outcome was assessed for total plasma protein and compared with CRIB, CRIB-II, SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II, by calculating receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and their associated area under the curve (AUC).
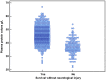
Results: 761 infants were studied: 14.4% died and 4.1% survived with severe cerebral ultrasound findings. The aOR of severe adverse outcome for hypoproteinemia was 6.1 (95% CI 3.8-9.9). The rank order for variables, as assessed by AUCs and 95% CIs, in predicting outcome was: total plasma protein [0.849 (0.821-0.873)], SNAPPE-II [0.822 (0.792-0.848)], CRIB [0.821 (0.792-0.848)], SNAP-II [0.810 (0.780-0.837)] and CRIB-II [0.803 (0.772-0.830)]. Total plasma protein predicted severe adverse outcome significantly better than CRIB-II and SNAP-II (both p<0.05). Calibration for total plasma protein was very good.
Conclusions: Early hypoproteinemia has prognostic value for severe adverse outcome in very preterm, sick infants. Total plasma protein has a predictive performance comparable with CRIB and SNAPPE-II and greater than other validated severity scores.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Bode MM, D'Eugenio DB, Forsyth N, Coleman J, Gross CR, et al. (2009) Outcome of extreme prematurity: a prospective comparison of 2 regional cohorts born 20 years apart. Pediatrics 124: 866–874. - PubMed
-
- van Haastert IC, Groenendaal F, Uiterwaal CS, Termote JU, van der Heide-Jalving M, et al. (2011) Decreasing incidence and severity of cerebral palsy in prematurely born children. J Pediatr 159: 86–91. - PubMed
-
- International Neonatal Network (1993) The CRIB (clinical risk index for babies) score: a tool for assessing initial neonatal risk and comparing performance of neonatal intensive care units. Lancet 342: 193–198. - PubMed
-
- Parry G, Tucker J, Tarnow-Mordi WO (2003) CRIB-II: an update of the clinical risk index for babies score. Lancet 361: 1789–1791. - PubMed
-
- Richardson DK, Corcoran JD, Escobar GJ, Lee SK (2001) SNAP-II and SNAPPE-II: Simplified newborn illness severity and mortality risk scores. J Pediatr 138: 92–100. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

