Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor is mediated by PI3-K/MEK1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
- PMID: 23615263
- PMCID: PMC4133881
- DOI: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.4.200
Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced expression of granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor is mediated by PI3-K/MEK1/p38 MAPK signaling pathway
Abstract
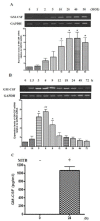
Members of the colony stimulating factor cytokine family play important roles in macrophage activation and recruitment to inflammatory lesions. Among them, granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF) is known to be associated with immune response to mycobacterial infection. However, the mechanism through which Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) affects the expression of GM-CSF is poorly understood. Using PMA-differentiated THP-1 cells, we found that MTB infection increased GM-CSF mRNA expression in a dosedependent manner. Induction of GM-CSF mRNA expression peaked 6 h after infection, declining gradually thereafter and returning to its basal levels at 72 h. Secretion of GM-CSF protein was also elevated by MTB infection. The increase in mRNA expression and protein secretion of GM-CSF caused by MTB was inhibited in cells treated with inhibitors of p38 MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK-1), and PI3-K. These results suggest that up-regulation of GM-CSF by MTB is mediated via the PI3-K/MEK1/p38 MAPK-associated signaling pathway.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. WHO report 2007: Global tuberculosis control; surveillance, planning, financing. WHO; Geneva: 2007. pp. 1–277.
-
- World Health Organization. WHO report 2007: Global MDR-TB and XDR-TB response plan 2007-2008. WHO; Geneva: 2007. pp. 1–48.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

