Differential effects of estradiol on carotid artery inflammation when administered early versus late after surgical menopause
- PMID: 23615645
- PMCID: PMC4594203
- DOI: 10.1097/GME.0b013e31827461e0
Differential effects of estradiol on carotid artery inflammation when administered early versus late after surgical menopause
Abstract
Objective: The aim of this study was to determine the effects of estrogen therapy (ET) on carotid artery inflammation when initiated early and late relative to surgical menopause.
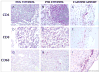
Methods: Female cynomolgus macaques consuming atherogenic diets were ovariectomized and randomized to control or oral estradiol (E2; human equivalent dose of 1 mg/d micronized E2) initiated at 1 month (early menopause, n = 24) or 54 months (late menopause, n = 40) after ovariectomy. The treatment period was 8 months. Carotid artery expression of the markers of monocyte/macrophages (CD68 and CD163), dendritic cells (CD83), natural killer cells (neural cell adhesion molecule-1), and interferon-γ was significantly lower in E2-treated animals in the early menopause group but not in the late menopause group (P < 0.05). In contrast, carotid artery transcripts for T-cell markers (CD3, CD4, CD8, and CD25), interleukin-10, type I collagen, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1, matrix metalloproteinase-9, and tumor necrosis factor-α were lower in E2-treated monkeys regardless of menopausal stage (P < 0.05).
Conclusions: ET initiated soon after menopause inhibits macrophage accumulation in the carotid artery, an effect that is not observed when E2 is administered after several years of estrogen deficiency. No evidence for pro-inflammatory effects of late ET is observed. The results provide support for the timing hypothesis of postmenopausal ET with implications for the interpretation of outcomes in the Women's Health Initiative.
Figures
References
-
- Hansson GK, Robertson AK, Soderberg-Naucler C. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2006;1:297–329. - PubMed
-
- Andersson J, Libby P, Hansson GK. Adaptive immunity and atherosclerosis. Clin Immunol. 2010;134(1):33–46. - PubMed
-
- Zhou X, Nicoletti A, Elhage R, Hansson GK. Transfer of CD4(+) T cells aggravates atherosclerosis in immunodeficient apolipoprotein E knockout mice. Circulation. 2000;102(24):2919–22. - PubMed
-
- Mendelsohn ME. Protective effects of estrogen on the cardiovascular system. Am J Cardiol. 2002;89(12A):12E–7E. discussion 7E–8E. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

