Overexpression of USP14 protease reduces I-κB protein levels and increases cytokine release in lung epithelial cells
- PMID: 23615914
- PMCID: PMC3668705
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.C112.446682
Overexpression of USP14 protease reduces I-κB protein levels and increases cytokine release in lung epithelial cells
Abstract
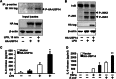
The ubiquitin-proteasome system is the major pathway of non-lysosomal intracellular protein degradation, playing an important role in a variety of cellular responses including cell division, proliferation, and apoptosis. Ubiquitin-specific protease 14 (USP14) is a component of proteasome regulatory subunit 19 S that regulates deubiquitinated proteins entering inside the proteasome core 20 S. The role of USP14 in protein degradation is still controversial. Several studies suggest that USP14 plays an inhibitory role in protein degradation. Here, in contrast, overexpression of USP14 induced I-κB degradation, which increased cytokine release in lung epithelial cells. Overexpression of HA-tagged USP14 (HA-USP14) reduced I-κB protein levels by increasing the I-κB degradation rate in mouse lung epithelial cells (MLE12). I-κB polyubiquitination was reduced in HA-USP14-overexpressed MLE12 cells, suggesting that USP14 regulates I-κB degradation by removing its ubiquitin chain, thus promoting the deubiquitinated I-κB degradation within the proteasome. Interestingly, we found that USP14 was associated with RelA, a binding partner of I-κB, suggesting that RelA is the linker between USP14 and I-κB. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) treatment induced serine phosphorylation of USP14 as well as further reducing I-κB levels in HA-USP14-overexpressed MLE12 cells as compared with empty vector transfected cells. Further, overexpression of HA-USP14 increased the LPS-, TNFα-, or Escherichia coli-induced IL-8 release in human lung epithelial cells. This study suggests that USP14 removes the ubiquitin chain of I-κB, therefore inducing I-κB degradation and increasing cytokine release in lung epithelial cells.
Keywords: Cytokine; Deubiquitination; NF-κB Transcription Factor; Protein Phosphorylation; Protein degradation; USP14.
Figures

References
-
- Hershko A., Ciechanover A. (1992) The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 61, 761–807 - PubMed
-
- Schwartz A. L., Ciechanover A. (1992) Ubiquitin-mediated protein modification and degradation. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 7, 463–468 - PubMed
-
- Ugai S., Tamura T., Tanahashi N., Takai S., Komi N., Chung C. H., Tanaka K., Ichihara A. (1993) Purification and characterization of the 26S proteasome complex catalyzing ATP-dependent breakdown of ubiquitin-ligated proteins from rat liver. J. Biochem. 113, 754–768 - PubMed
-
- Saeki Y., Tanaka K. (2012) Assembly and function of the proteasome. Methods Mol. Biol. 832, 315–337 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

