Associations of total and undercarboxylated osteocalcin with peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in overweight adults
- PMID: 23616149
- PMCID: PMC3701277
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2013-1203
Associations of total and undercarboxylated osteocalcin with peripheral and hepatic insulin sensitivity and β-cell function in overweight adults
Erratum in
-
Corrigenda.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016 May;101(5):2265. doi: 10.1210/jc.2016-1578. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2016. PMID: 27163465 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Context: Animal studies indicate that osteocalcin (OC), particularly the undercarboxylated isoform (unOC), affects insulin sensitivity and secretion, but definitive data from humans are lacking.
Objective: The objectives of the study were to determine whether total OC and unOC are independently associated with insulin sensitivity and β-cell response in overweight/obese adults; whether glucose tolerance status affects these associations; and whether the associations are independent of bone formation, as reflected in procollagen type 1 amino propeptide (P1NP).
Design, setting, and participants: This was a cross-sectional study conducted at a university research center involving 63 overweight/obese adults with normal (n = 39) or impaired fasting glucose (IFG; n = 24).
Main outcome measures: Serum concentrations of total/undercarboxylated OC and P1NP were assessed by RIA; insulin sensitivity was determined by iv glucose tolerance test (S(I)-IVGTT), liquid meal test (S(I) meal), and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; β-cell response to glucose [basal β-cell response to glucose; dynamic β-cell response to glucose; static β-cell response to glucose; and total β-cell response to glucose] was derived using C-peptide modeling of meal test data; and intraabdominal adipose tissue was measured using computed tomography scanning.
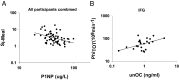
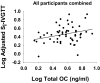
Results: Multiple linear regression, adjusting for intraabdominal adipose tissue and P1NP, revealed that total OC was positively associated with S(I)-iv glucose tolerance test (P < .01) in the total sample. OC was not associated with S(I) meal or homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance. In participants with IFG, unOC was positively associated with static β-cell response to glucose and total β-cell response to glucose (P < .05), independent of insulin sensitivity.
Conclusions: In overweight/obese individuals, total OC may be associated with skeletal muscle but not hepatic insulin sensitivity. unOC is uniquely associated with β-cell function only in individuals with IFG. Further research is needed to probe the causal inference of these relationships and to determine whether indirect nutrient sensing pathways underlie these associations.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00726908.
Figures
References
-
- Hauschka PV, Lian JB, Cole DE, Gundberg CM. Osteocalcin and matrix Gla protein: vitamin K-dependent proteins in bone. Physiol Rev. 1989;69:990–1047 - PubMed
-
- Ducy P. The role of osteocalcin in the endocrine cross-talk between bone remodelling and energy metabolism. Diabetologia. 2011;54:1291–1297 - PubMed
-
- Clemens TL, Karsenty G. The osteoblast: an insulin target cell controlling glucose homeostasis. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26:677–680 - PubMed
-
- Hwang YC, Jeong IK, Ahn KJ, Chung HY. The uncarboxylated form of osteocalcin is associated with improved glucose tolerance and enhanced β-cell function in middle-aged male subjects. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2009;25:768–772 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- R01DK67538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01HL87923-03S1/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- M01-RR-00032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK079637/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087923/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-DK56336/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK062710/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000032/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1RR025777/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R24 DK084949/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK067538/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30-AR46031/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P60DK079626/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AR046031/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK056336/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- L40 HL110299/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

