Domain organization of membrane-bound factor VIII
- PMID: 23616213
- PMCID: PMC4090243
- DOI: 10.1002/bip.22199
Domain organization of membrane-bound factor VIII
Abstract
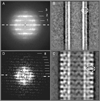
Factor VIII (FVIII) is the blood coagulation protein which when defective or deficient causes for hemophilia A, a severe hereditary bleeding disorder. Activated FVIII (FVIIIa) is the cofactor to the serine protease factor IXa (FIXa) within the membrane-bound Tenase complex, responsible for amplifying its proteolytic activity more than 100,000 times, necessary for normal clot formation. FVIII is composed of two noncovalently linked peptide chains: a light chain (LC) holding the membrane interaction sites and a heavy chain (HC) holding the main FIXa interaction sites. The interplay between the light and heavy chains (HCs) in the membrane-bound state is critical for the biological efficiency of FVIII. Here, we present our cryo-electron microscopy (EM) and structure analysis studies of human FVIII-LC, when helically assembled onto negatively charged single lipid bilayer nanotubes. The resolved FVIII-LC membrane-bound structure supports aspects of our previously proposed FVIII structure from membrane-bound two-dimensional (2D) crystals, such as only the C2 domain interacts directly with the membrane. The LC is oriented differently in the FVIII membrane-bound helical and 2D crystal structures based on EM data, and the existing X-ray structures. This flexibility of the FVIII-LC domain organization in different states is discussed in the light of the FVIIIa-FIXa complex assembly and function.
Copyright © 2013 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Dimeric Organization of Blood Coagulation Factor VIII bound to Lipid Nanotubes.Sci Rep. 2015 Jun 17;5:11212. doi: 10.1038/srep11212. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26082135 Free PMC article.
-
Helical organization of blood coagulation factor VIII on lipid nanotubes.J Vis Exp. 2014 Jun 3;(88):51254. doi: 10.3791/51254. J Vis Exp. 2014. PMID: 24961276 Free PMC article.
-
Lack of recombinant factor VIII B-domain induces phospholipid vesicle aggregation: implications for the immunogenicity of factor VIII.Haemophilia. 2014 Sep;20(5):723-31. doi: 10.1111/hae.12421. Epub 2014 Apr 21. Haemophilia. 2014. PMID: 24750465 Free PMC article.
-
Role of activation of the coagulation factor VIII in interaction with vWf, phospholipid, and functioning within the factor Xase complex.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999 Oct;9(7):185-92. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(00)00019-0. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 1999. PMID: 10881749 Review.
-
Factor VIII and Factor V Membrane Bound Complexes.Subcell Biochem. 2021;96:153-175. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-58971-4_2. Subcell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33252728 Review.
Cited by
-
SAXS analysis of the intrinsic tenase complex bound to a lipid nanodisc highlights intermolecular contacts between factors VIIIa/IXa.Blood Adv. 2022 Jun 14;6(11):3240-3254. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021005874. Blood Adv. 2022. PMID: 35255502 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering Membrane-Bound Models of Coagulation Factors by Combined Experimental and Computational Approaches.Thromb Haemost. 2021 Sep;121(9):1122-1137. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1722187. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Thromb Haemost. 2021. PMID: 34214998 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure of coagulation factor VIII bound to a patient-derived anti-C1 domain antibody inhibitor.Blood. 2023 Jul 13;142(2):197-201. doi: 10.1182/blood.2023020181. Blood. 2023. PMID: 37192299 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and laboratory approaches to hemophilia a.Iran J Med Sci. 2015 May;40(3):194-205. Iran J Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 25999618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular engineering of cyclic azobenzene-peptide hybrid ligands for the purification of human blood Factor VIII via photo-affinity chromatography.Adv Funct Mater. 2023 Apr 4;33(14):2213881. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202213881. Epub 2023 Jan 25. Adv Funct Mater. 2023. PMID: 37576949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toole JJ, Knopf JL, et al. Nature. 1984;312:342–347. - PubMed
-
- Vehar GA, Keyt B, et al. Nature. 1984;312:337–342. - PubMed
-
- Kane WH, Davie EW. Blood. 1988;71:539–555. - PubMed
-
- Lenting PJ, Mourik JA, Mertens K. Blood. 1998;92:3983–9396. - PubMed
-
- Pemberton S, Lindley P, Zaitsev V, Xard G, Tuddenham EG, Kemball-Cook G. Blood. 1997;89:2413–2421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

