Endemic genotypes of Candida albicans causing fungemia are frequent in the hospital
- PMID: 23616451
- PMCID: PMC3697706
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.00516-13
Endemic genotypes of Candida albicans causing fungemia are frequent in the hospital
Abstract
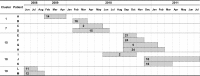
Genotyping of Candida albicans strains causing candidemia can uncover the presence of endemic genotypes in the hospital. Using a highly reproducible and discriminatory microsatellite marker panel, we studied the genetic diversity of 217 C. albicans isolates from the blood cultures of 202 patients with candidemia (from January 2007 to December 2011). Each isolate represented 1 candidemia episode. Multiple episodes were defined as the isolation of C. albicans in further blood cultures taken ≥7 days after the last isolation in blood culture. Of the 202 patients, 188 had 1 episode, 13 had 2 episodes, and 1 had 3 episodes. Identical genotypes showed the same alleles for all 6 markers. The genotypes causing both episodes were identical in most patients with 2 episodes (11/13; 84.6%). In contrast, 2 different genotypes were found in the patient with 3 episodes, one causing the first and second episodes and the other causing the third episode (isolated 6 months later). We found marked genetic diversity in 174 different genotypes: 155 were unique, and 19 were endemic and formed 19 clusters (2 to 6 patients per cluster). Up to 25% of the patients were infected by endemic genotypes that infected 2 or more different patients. Some of these endemic genotypes were found in the same unit of the hospital, mainly neonatology, whereas others infected patients in different wards.
Figures


References
-
- Arendrup MC, Bruun B, Christensen JJ, Fuursted K, Johansen HK, Kjaeldgaard P, Knudsen JD, Kristensen L, Moller J, Nielsen L, Rosenvinge FS, Roder B, Schonheyder HC, Thomsen MK, Truberg K. 2011. National surveillance of fungemia in Denmark (2004 to 2009). J. Clin. Microbiol. 49:325–334 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Leroy O, Gangneux JP, Montravers P, Mira JP, Gouin F, Sollet JP, Carlet J, Reynes J, Rosenheim M, Regnier B, Lortholary O. 2009. Epidemiology, management, and risk factors for death of invasive Candida infections in critical care: a multicenter, prospective, observational study in France (2005-2006). Crit. Care Med. 37:1612–1618 - PubMed
-
- Neofytos D, Fishman JA, Horn D, Anaissie E, Chang CH, Olyaei A, Pfaller M, Steinbach WJ, Webster KM, Marr KA. 2010. Epidemiology and outcome of invasive fungal infections in solid organ transplant recipients. Transpl Infect. Dis. 12:220–229 - PubMed
-
- Peman J, Canton E, Quindos G, Eraso E, Alcoba J, Guinea J, Merino P, Ruiz-Perez-de-Pipaon MT, Perez-del-Molino L, Linares-Sicilia MJ, Marco F, Garcia J, Rosello EM, Gomez E, Borrell N, Porras A, Yague G. 2012. Epidemiology, species distribution, and in vitro antifungal susceptibility of fungaemia in a Spanish multicentre prospective survey. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 67:1181–1187 - PubMed
-
- Pfaller MA, Moet GJ, Messer SA, Jones RN, Castanheira M. 2011. Candida bloodstream infections: comparison of species distributions and antifungal resistance patterns in community-onset and nosocomial isolates in the SENTRY Antimicrobial Surveillance Program, 2008-2009. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 55:561–566 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

