Splicing kinetics and transcript release from the chromatin compartment limit the rate of Lipid A-induced gene expression
- PMID: 23616639
- PMCID: PMC3683915
- DOI: 10.1261/rna.039081.113
Splicing kinetics and transcript release from the chromatin compartment limit the rate of Lipid A-induced gene expression
Abstract
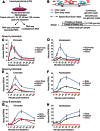
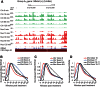
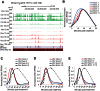
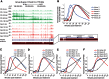
The expression of eukaryotic mRNAs is achieved though an intricate series of molecular processes that provide many steps for regulating the production of a final gene product. However, the relationships between individual steps in mRNA biosynthesis and the rates at which they occur are poorly understood. By applying RNA-seq to chromatin-associated and soluble nucleoplasmic fractions of RNA from Lipid A-stimulated macrophages, we examined the timing of exon ligation and transcript release from chromatin relative to the induction of transcription. We find that for a subset of genes in the Lipid A response, the ligation of certain exon pairs is delayed relative to the synthesis of the complete transcript. In contrast, 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation occur rapidly once transcription extends through the cleavage site. Our data indicate that these transcripts with delayed splicing are not released from the chromatin fraction until all the introns have been excised. These unusual kinetics result in a chromatin-associated pool of completely transcribed and 3'-processed transcripts that are not yet fully spliced. We also find that long introns containing repressed exons that will be excluded from the final mRNA are excised particularly slowly relative to other introns in a transcript. These results indicate that the kinetics of splicing and transcript release contribute to the timing of expression for multiple genes of the inflammatory response.
Keywords: gene expression; inflammatory response; mRNA maturation; pre-mRNA splicing; splicing kinetics.
Figures
References
-
- Alexander RD, Barrass JD, Dichtl B, Kos M, Obtulowicz T, Robert MC, Koper M, Karkusiewicz I, Mariconti L, Tollervey D, et al. 2010a. RiboSys, a high-resolution, quantitative approach to measure the in vivo kinetics of pre-mRNA splicing and 3′-end processing in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RNA 16: 2570–2580 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ameur A, Zaghlool A, Halvardson J, Wetterbom A, Gyllensten U, Cavelier L, Feuk L 2011. Total RNA sequencing reveals nascent transcription and widespread co-transcriptional splicing in the human brain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 18: 1435–1440 - PubMed
-
- Ardehali MB, Lis JT 2009. Tracking rates of transcription and splicing in vivo. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16: 1123–1124 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
