Increased polyamines alter chromatin and stabilize autoantigens in autoimmune diseases
- PMID: 23616785
- PMCID: PMC3627976
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2013.00091
Increased polyamines alter chromatin and stabilize autoantigens in autoimmune diseases
Abstract
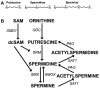
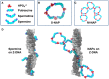
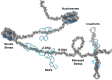
Polyamines are small cations with unique combinations of charge and length that give them many putative interactions in cells. Polyamines are essential since they are involved in replication, transcription, translation, and stabilization of macro-molecular complexes. However, polyamine synthesis competes with cellular methylation for S-adenosylmethionine, the methyl donor. Also, polyamine degradation can generate reactive molecules like acrolein. Therefore, polyamine levels are tightly controlled. This control may be compromised in autoimmune diseases since elevated polyamine levels are seen in autoimmune diseases. Here a hypothesis is presented explaining how polyamines can stabilize autoantigens. In addition, the hypothesis explains how polyamines can inappropriately activate enzymes involved in NETosis, a process in which chromatin is modified and extruded from cells as extracellular traps that bind pathogens during an immune response. This polyamine-induced enzymatic activity can lead to an increase in NETosis resulting in release of autoantigenic material and tissue damage.
Keywords: NETosis; autoimmune disease; neutrophil extracellular TRAPs; nuclear aggregates of polyamines; peptidylarginine deiminase; polyamines.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Autoimmune diseases and polyamines.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012 Feb;42(1):58-70. doi: 10.1007/s12016-011-8290-y. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2012. PMID: 22116709 Review.
-
The mysterious polyamines, the enigmatic Barr body, and lupus: comment on the article by Kim et al.Lupus. 2018 May;27(6):877-879. doi: 10.1177/0961203318757929. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Lupus. 2018. PMID: 29444615
-
Polyamine homoeostasis.Essays Biochem. 2009 Nov 4;46:11-24. doi: 10.1042/bse0460002. Essays Biochem. 2009. PMID: 20095967 Review.
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus and related autoimmune diseases are antigen-driven, epigenetic diseases.Med Hypotheses. 2002 Dec;59(6):736-41. doi: 10.1016/s0306-9877(02)00322-5. Med Hypotheses. 2002. PMID: 12445518
-
Polyamine--DNA nexus: structural ramifications and biological implications.Mol Cell Biochem. 1991 Feb 2;100(2):129-40. doi: 10.1007/BF00234162. Mol Cell Biochem. 1991. PMID: 2008175 Review.
Cited by
-
Ablation of polyamine catabolic enzymes provokes Purkinje cell damage, neuroinflammation, and severe ataxia.J Neuroinflammation. 2020 Oct 14;17(1):301. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-01955-6. J Neuroinflammation. 2020. PMID: 33054763 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics and autoimmune diseases: the X chromosome-nucleolus nexus.Front Genet. 2015 Feb 16;6:22. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2015.00022. eCollection 2015. Front Genet. 2015. PMID: 25763008 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Autoimmune Disease Hypotheses with Introduction of the "Nucleolus" Hypothesis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017 Jun;52(3):333-350. doi: 10.1007/s12016-016-8567-2. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2017. PMID: 27324247 Review.
-
Plasma S-Adenosylmethionine Is Associated with Lung Injury in COVID-19.Dis Markers. 2021 Dec 16;2021:7686374. doi: 10.1155/2021/7686374. eCollection 2021. Dis Markers. 2021. PMID: 34956420 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic modeling of single Th17 cells reveals regulators of autoimmunity.Cell. 2021 Aug 5;184(16):4168-4185.e21. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.05.045. Epub 2021 Jul 2. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34216539 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

