A review of medication reconciliation issues and experiences with clinical staff and information systems
- PMID: 23616853
- PMCID: PMC3633312
- DOI: 10.4338/ACI-2010-02-R-0010
A review of medication reconciliation issues and experiences with clinical staff and information systems
Abstract
Medication reconciliation was developed to reduce medical mistakes and injuries through a process of creating and comparing a current medication list from independent patient information sources, and resolving discrepancies. The structure and clinician assignments of medication reconciliation varies between institutions, but usually includes physicians, nurses and pharmacists. The Joint Commission has recognized the value of medication reconciliation and mandated implementation in 2006; however, a variety of issues have prevented simple, easy, and universal implementation. This review references issues related to the development and the implementation of medication reconciliation including: - the need of a system or standard for accurate drug identification to create a definitive 'gold standard' patient medication list, - identifying stakeholders of medication reconciliation within the institution and contrasting staff interest and participation with institutional resources, - observations and opportunities of integrating medication reconciliation with the electronic patient health record, and - summarizing a series of institutions experiences developing and implementing medication reconciliation. Last, as medication reconciliation becomes a regular process within medical centers, key concepts for effective implementation are discussed.
Keywords: Medication reconciliation; drug errors; medical errors; medical informatics; patient safety; pharmaceuticals.
Figures

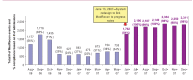
References
-
- Kohn KT, Corrigan JM, Donaldson MS. To err is human: Building a safer health system. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 1999 - PubMed
-
- Institute of Medicine Crossing the quality chasm: a new health care system for the 21st century. Washington, DC: National Academy Press; 2001
-
- Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality . Medical errors: The scope of the problem. Publication No.AHRQ 00-PO37 accessed 1/2/2010
-
- The Joint Commission Using medication reconciliation to prevent errors. Jt Comm J Qual Patient Saf 2006; 32: 230-232 PMID:16649655 - PubMed
-
- Pronovost P, Weast B, Schwarz M, Wyskiel RM, Prow D, Milanovich SN, et al. Medication reconciliation: a practical tool to reduce the risk of medication errors. J Crit Care 2003; 18: 201-205 PMID:14691892 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

