Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan stem packing by rotational-echo double resonance NMR spectroscopy
- PMID: 23617832
- PMCID: PMC3796188
- DOI: 10.1021/bi4005039
Staphylococcus aureus peptidoglycan stem packing by rotational-echo double resonance NMR spectroscopy
Abstract
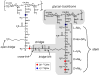
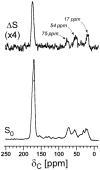
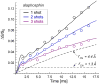
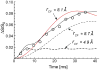
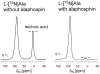
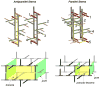
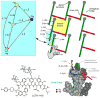
Staphylococcus aureus grown in the presence of an alanine-racemase inhibitor was labeled with d-[1-(13)C]alanine and l-[(15)N]alanine to characterize some details of the peptidoglycan tertiary structure. Rotational-echo double-resonance NMR of intact whole cells was used to measure internuclear distances between (13)C and (15)N of labeled amino acids incorporated in the peptidoglycan, and from those labels to (19)F of a glycopeptide drug specifically bound to the peptidoglycan. The observed (13)C-(15)N average distance of 4.1-4.4 Å between d- and l-alanines in nearest-neighbor peptide stems is consistent with a local, tightly packed, parallel-stem architecture for a repeating structural motif within the peptidoglycan of S. aureus.
Figures
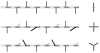
References
-
- Rogers HJ, Ward JB, Perkins HR. Microbial cell walls and membranes. Chapman and Hall; London; New York: 1980.
-
- van Heijenoort J. Formation of the glycan chains in the synthesis of bacterial peptidoglycan. Glycobiology. 2001;11:25R–36R. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

